Cancer
-
Ascus (bethesda System)
The Bethesda system (TBS), officially called The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology, is a system for reporting cervical or vaginal cytologic diagnoses,[1] used for reporting Pap smear results. It was introduced in 1988[2] and revised in 1991,[3] 2001,[1][4][5] and 2014.[6] The name… Read more.
-
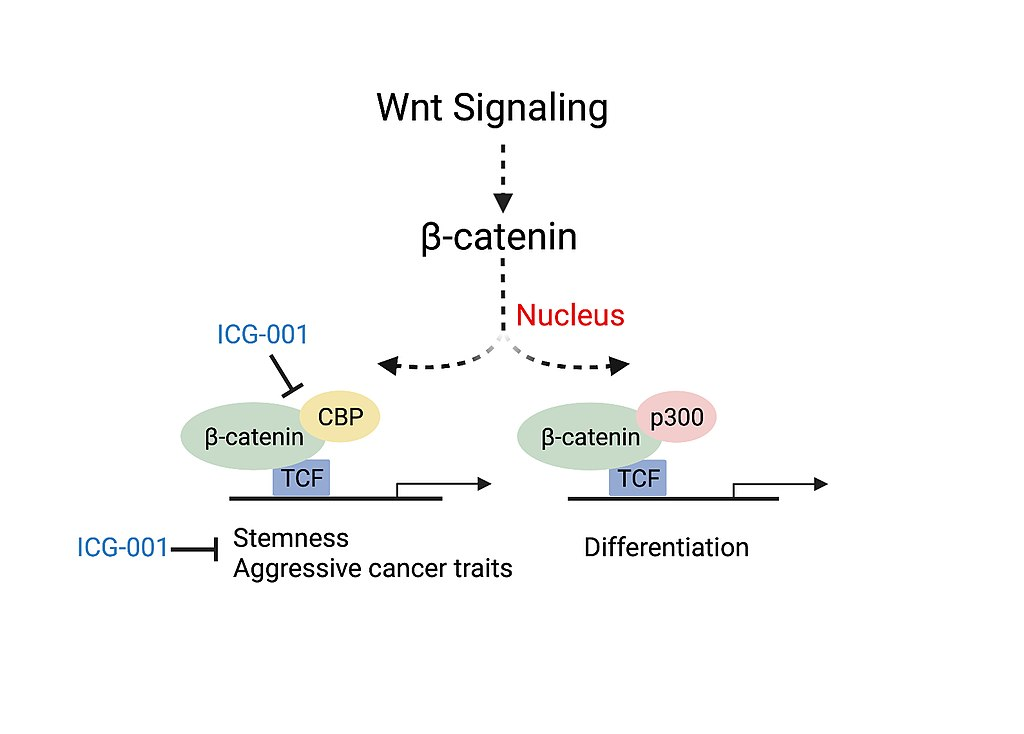
p300-CBP coactivator family – clinical significance
Mutations in CBP, and to a lesser extent p300, are the cause of Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome, which is characterized by severe mental retardation. These mutations result in the loss of one copy of… Read more.
-
Histone acetyltransferase p300
Histone acetyltransferase p300 also known as p300 HAT or E1A-associated protein p300 (where E1A = adenovirus early region 1A) also known as EP300 or p300 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the EP300 gene. It functions as histone acetyltransferase that regulates transcription of genes… Read more.
-
CBP has been shown to play a role in every stage of tumor development
Due to its critical role in regulation of cell proliferation, growth, migration and apoptosis, it is considered to be an oncogene, or tumor suppressor. Contrarily To date, increased CBP activity has been… Read more.
-
CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate Response Element Binding protein Binding Protein (CREB-binding protein), also known as CREBBP or CBP or KAT3A, is a coactivator encoded by the CREBBP gene in humans, located on chromosome 16p13.3. CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions; it is able to add acetyl groups to both… Read more.