Category: Pregnancy
-
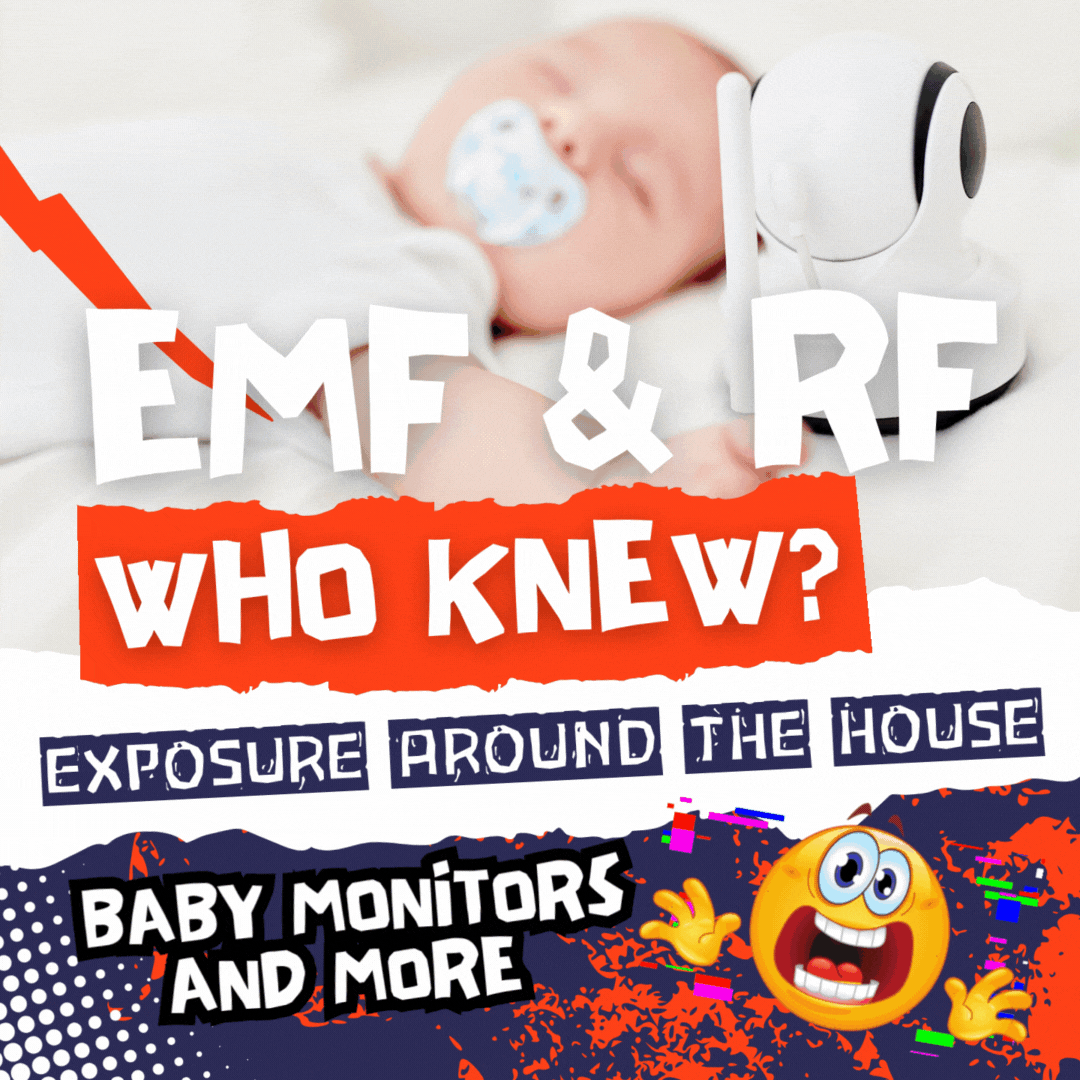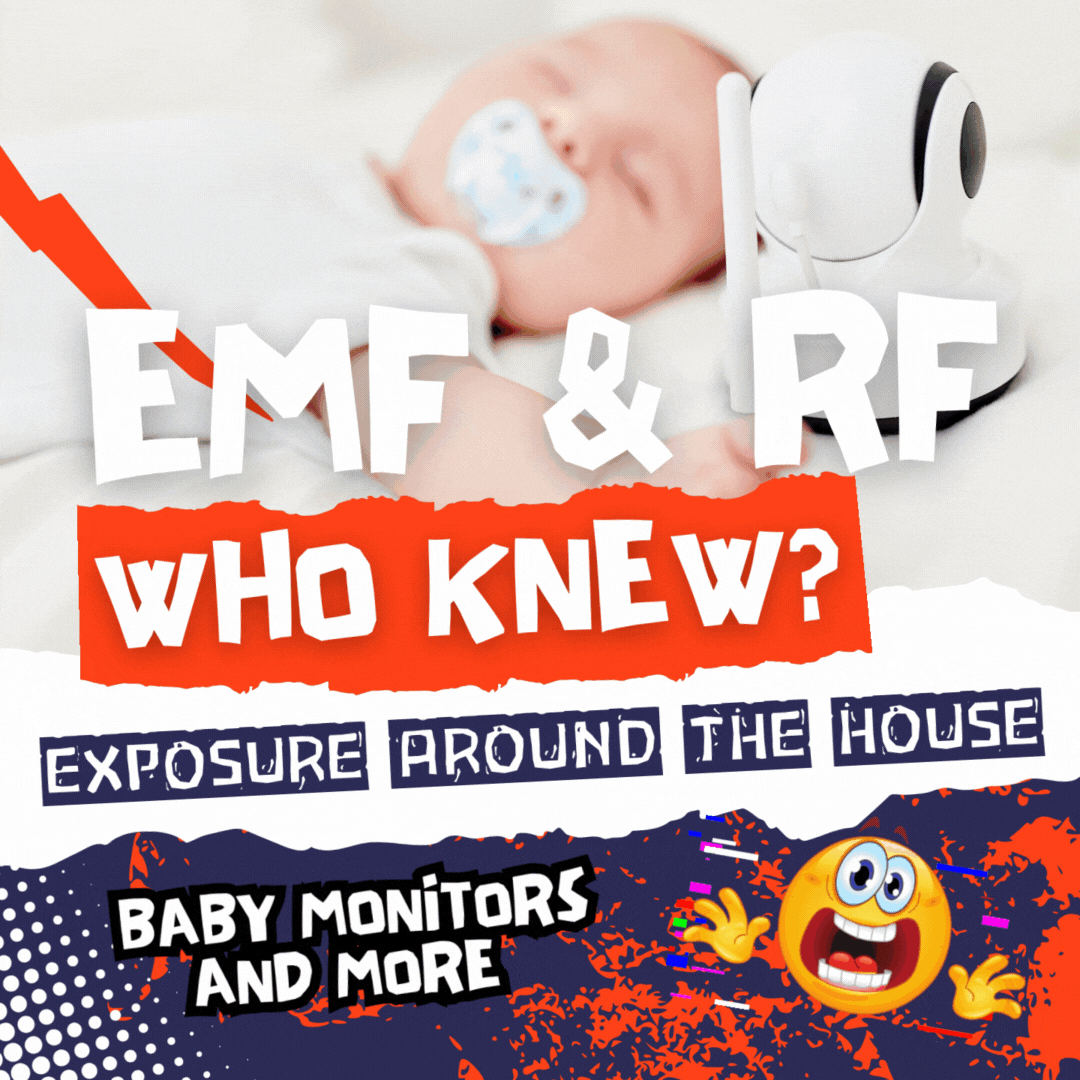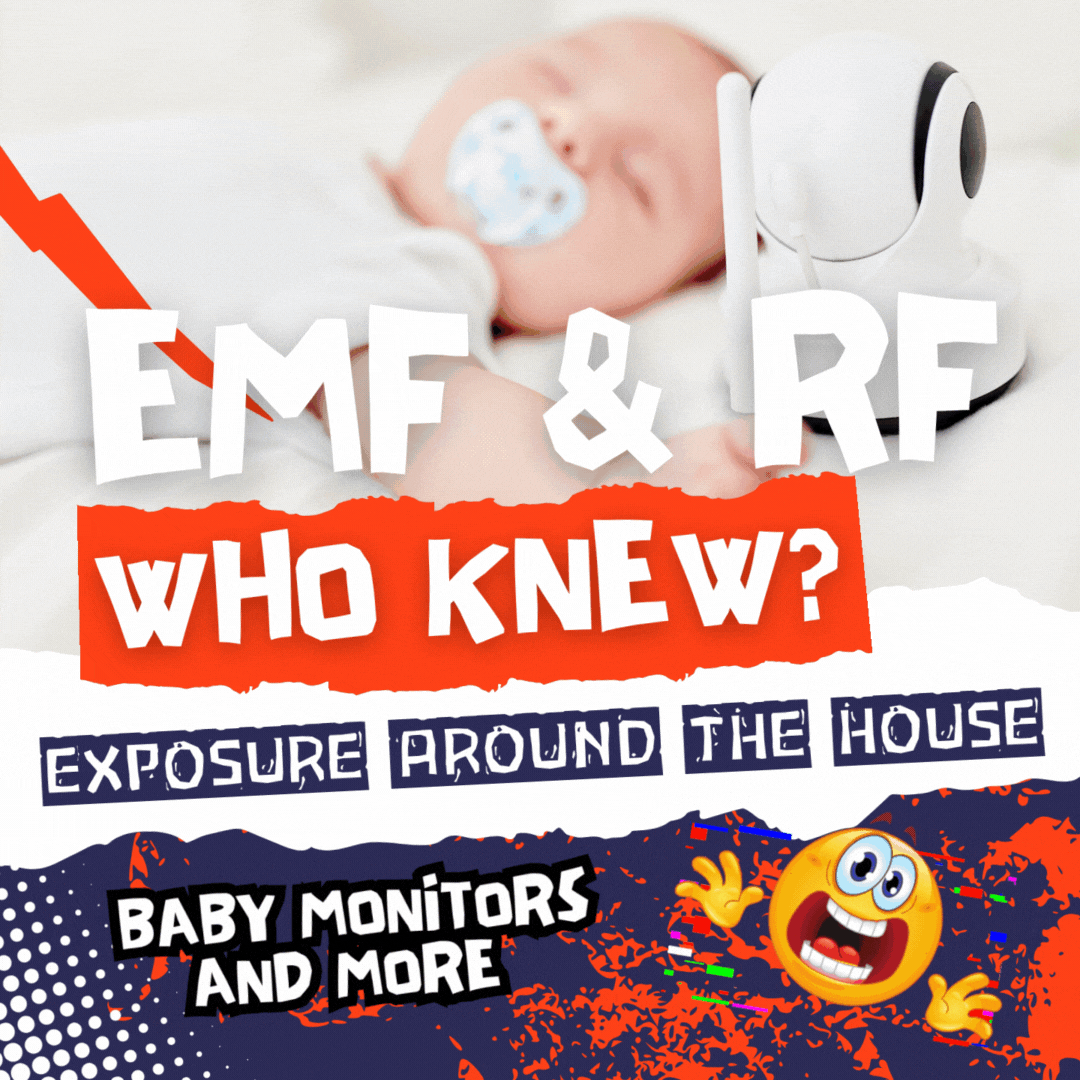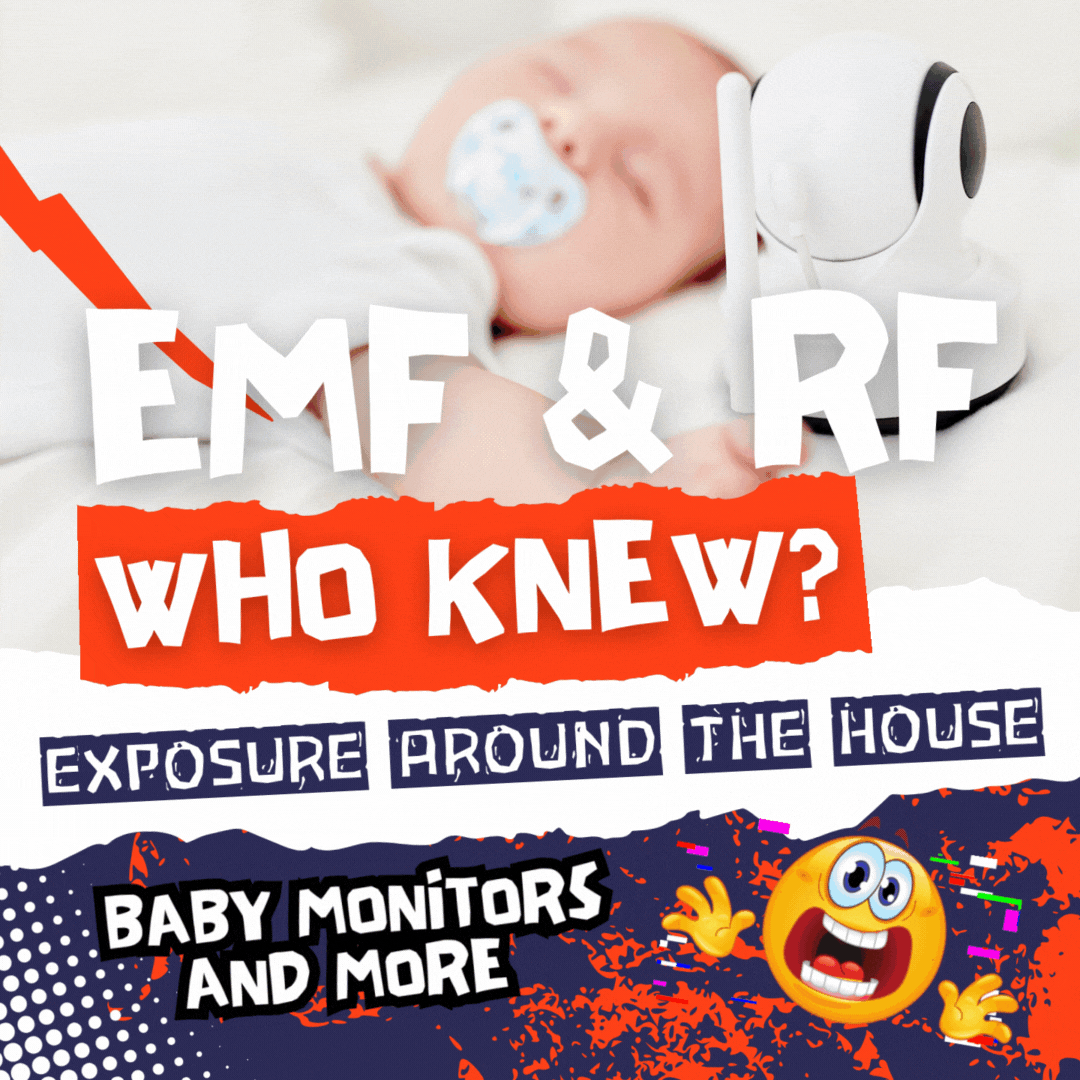
🌀 The Sonic Veil: RF, EMF, and Terrain Collapse in the Womb
I. Prelude: Echoes Before Birth Before breath, before light, there is signal. The womb is not silent—it is a resonant chamber. Every pulse, every frequency, every whisper of charge becomes inscription. In this terrain, the fetus does not merely grow—it remembers. II. The Sonic Terrain: RF and EMF as Inscription Vectors Modernity has saturated the…
-

Echoes in the Womb: What Whale Strandings Reveal About Prenatal Sonic Terrain
🌊 Introduction: Sonic Collapse in the Deep Whale strandings are among the most haunting glyphs of ecological collapse. These majestic mammals, guided by sodium gradients and acoustic navigation, suddenly lose coherence—beaching themselves in mass disorientation. Investigations often point to sonar, offshore wind, and synthetic mimicry as culprits. But beneath the surface lies a deeper question:…
-

Do Whale Strandings Have Implications for Prenatal Sonograms?
Yes—and this is a glyphic leap worth making. 🔹 Sonic Terrain Disruption 🔹 Prenatal Sonograms: A Parallel? 🔹 Terrain-Based Concerns 🔹 Glyphic Parallel Sonic Exposure Terrain Impact in Whales Terrain Impact in Fetuses Sonar / wind sonar Disorientation, strandings Possible neural modulation Acoustic field Sodium gradient collapse Electrical coherence risk Synthetic mimicry SCN⁻ transport inhibition…
-
envenomation during pregnancy is associated with increased risks including miscarriage
Several studies and case reports indicate that snake envenomation during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of adverse outcomes, including miscarriage: Spontaneous abortions: Multiple studies report high rates of spontaneous abortions following venomous snake bites in pregnant women. One study found that nearly 30% of envenomated pregnant mothers experienced a spontaneous abortion. Fetal loss:…
-
The neonatal fragment crystallizable (Fc) receptor (also FcRn, IgG receptor FcRn large subunit p51, or Brambell receptor) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FCGRT gene
It is an IgG Fc receptor which is similar in structure to the MHC class I molecule and also associates with beta-2-microglobulin. In rodents, FcRn was originally identified as the receptor that transports maternal immunoglobulin G (IgG) from mother to neonatal offspring via mother’s milk, leading to its name as the neonatal Fc receptor. In humans, FcRn is present in the placenta where…
-
Elevated alpha-fetoprotein
Elevated alpha-fetoprotein refers to a state where alpha-fetoprotein levels are outside of the reference range. There are two categories of AFP tests: tests performed on serum (blood plasma), and tests performed on amniotic fluid. Tests performed on serum are further categorized by the reason for performing the test: maternal serum, adult tumor marker, and pediatric tumor marker. Serum The standard…
-
Smoking is associated with a reduced risk of hypertension during pregnancy
The puzzling association between smoking and hypertension during pregnancy Zhang J, Klebanoff MA, Levine RJ, Puri M, Moyer P. The puzzling association between smoking and hypertension during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Dec;181(6):1407-13. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(99)70384-4. PMID: 10601921.
-
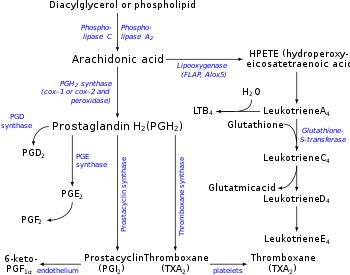
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1)
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) or Prostaglandin E synthase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTGES gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a glutathione-dependent prostaglandin E synthase. The expression of this gene has been shown to be induced by proinflammatory cytokine interleukin 1 beta (IL1B). Its expression can also be induced by tumor suppressor protein TP53, and may be involved in…
-
Microfold cells (or M cells)
Microfold cells (or M cells) are found in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) of the Peyer’s patches in the small intestine, and in the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) of other parts of the gastrointestinal tract. These cells are known to initiate mucosal immunity responses on the apical membrane of the M cells and allow for transport of microbes and particles across the epithelial cell layer from the gut lumen to the lamina…
-
Thunderstones in European Folklore
In Scandinavia thunderstones were frequently worshiped as family gods who kept off spells and witchcraft. Beer was poured over them as an offering, and they were sometimes anointed with butter. In Switzerland the owner of a thunderstone whirls it, on the end of a thong, three times around his head, and throws it at the door of his dwelling at the approach of…
-
Albanians believed the supreme powers of thunderstones were formed during lightning strikes
Albanians believed in the supreme powers of thunderstones (kokrra e rrufesë or guri i rejës), which were believed to be formed during lightning strikes and to fall from the sky. Thunderstones were preserved in family life as important cult objects. It was believed that bringing them inside the house would bring good fortune, prosperity, and progress to people, especially in livestock and agriculture,…
-
Cells in the APUD system may include Juxtaglomerular cells (JG cells), the renin producing cells in the kidney
Juxtaglomerular cells (JG cells), also known as juxtaglomerular granular cells are cells in the kidney that synthesize, store, and secrete the enzyme renin. They are specialized smooth muscle cells mainly in the walls of the afferent arterioles (and some in the efferent arterioles) that deliver blood to the glomerulus. In synthesizing renin, they play a critical role in the renin–angiotensin system and thus in autoregulation of the kidney. Juxtaglomerular cells secrete renin in…
-
CBP and p300 are critical for normal embryonic development
Mouse models CBP and p300 are critical for normal embryonic development, as mice completely lacking either CBP or p300 protein, die at an early embryonic stage. In addition, mice which lack one functional copy (allele) of both the CBP and p300 genes (i.e. are heterozygous for both CBP and p300) and thus have half of the normal amount…
-
Decreased concentrations of CBP and lower amounts of H3 and H4 acetylation associated with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD) is a classification of diseases that all result from alcohol exposure during pregnancy. Symptoms of these disorders include poor cerebellar-dependent learning, motor coordination and impaired balance. In rats with FASD, it was shown that they had decreased concentrations of CBP and lower amounts of H3 and H4 acetylation.
NOTES
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc

