Crystal Habit
-
Reniform – Kidney-shaped masses
Common examples include: cassiterite, chalcedony, chrysocolla, hematite, fluorite, goethite, greenockite, malachite, wavellite, mottramite Read more.
-
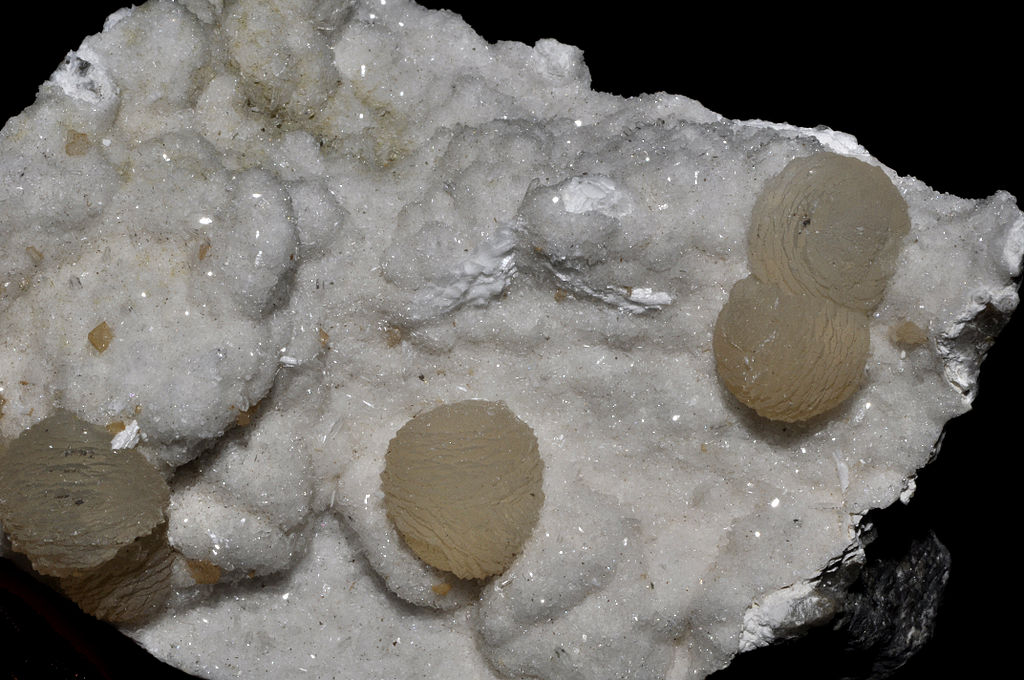
Mammillary – Breast-like: surface formed by intersecting partial spherical shapes, larger version of botryoidal and/or reniform, also concentric layered aggregates. It is almost synonymous with reniform.
Common examples include: chalcedony, hematite, malachite Read more.
-
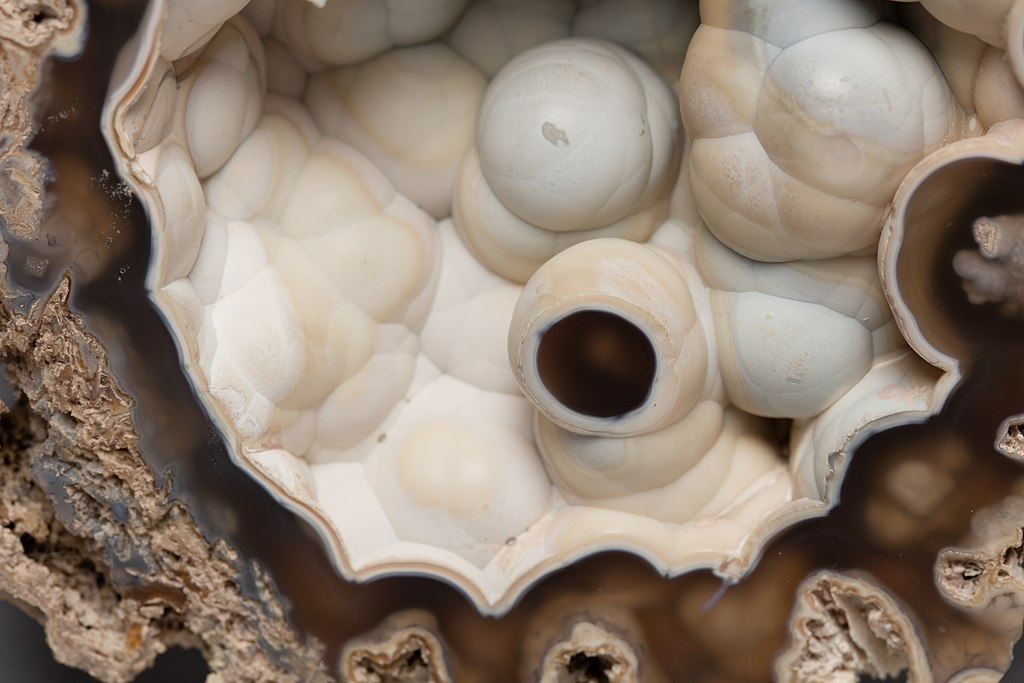
Globular – Isolated hemispheres or spheres
Common examples include: calcite, fluorite, gyrolite Read more.
-
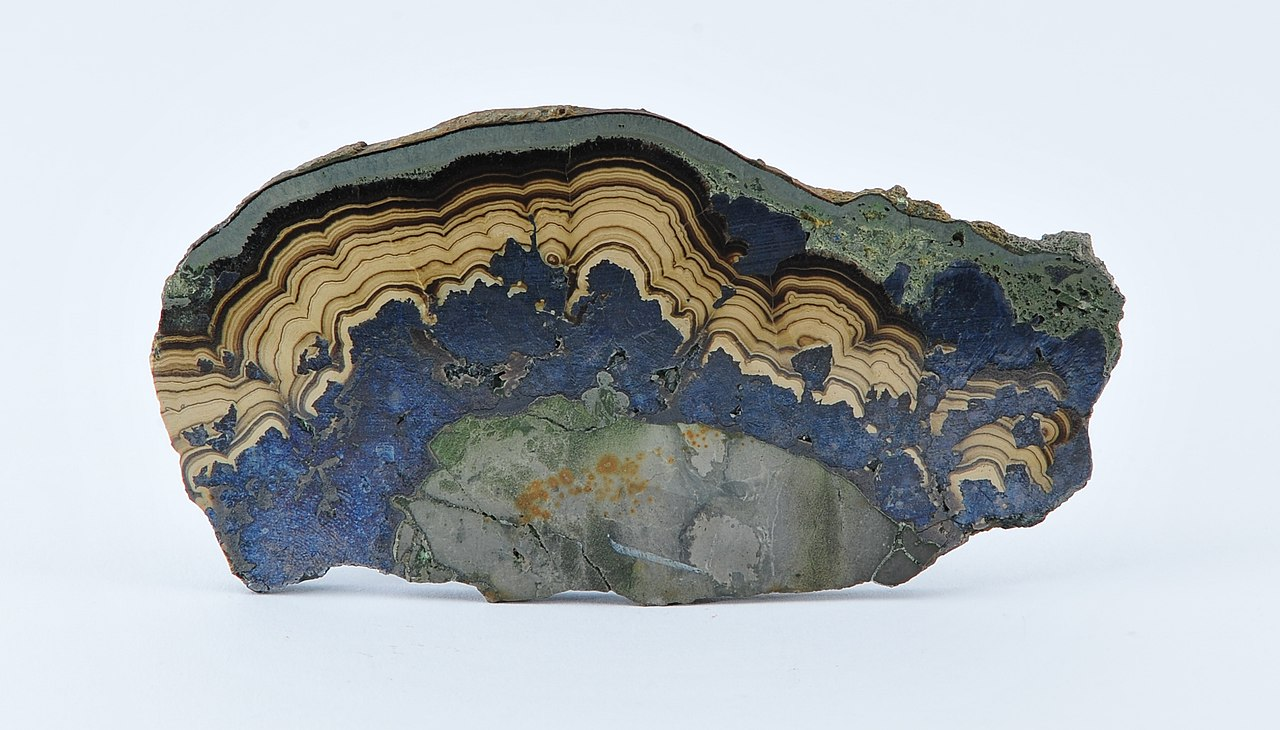
Colloform – Rounded, finely banded
Common examples include: sphalerite, pyrite Read more.
-
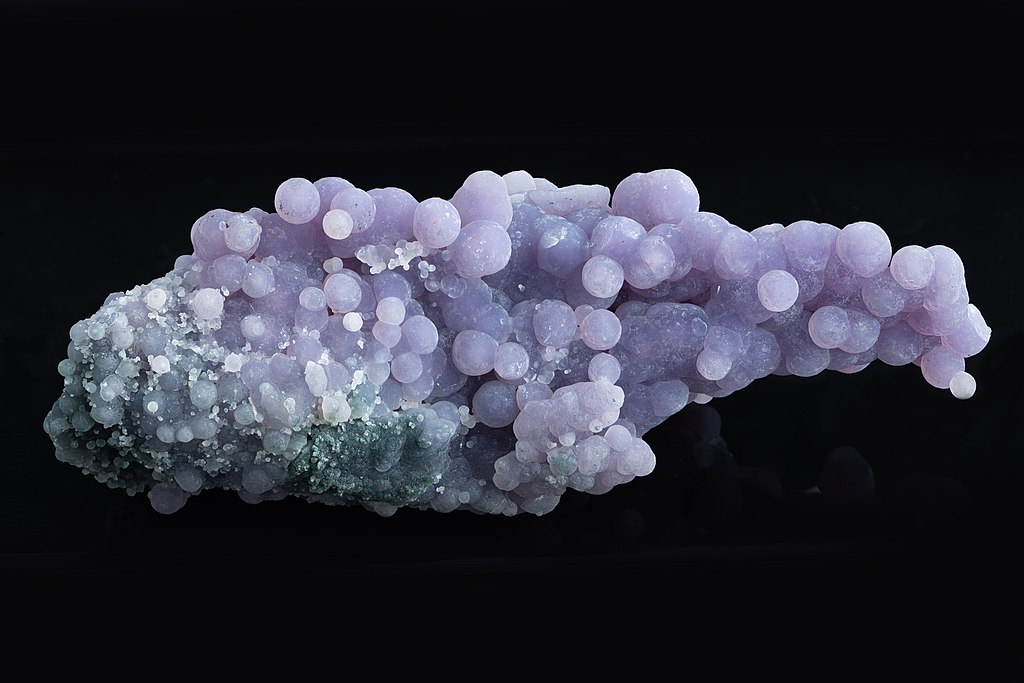
Botryoidal – Grape-like, large and small hemispherical masses, nearly differentiated/separated from each other
Common examples include: chalcedony, pyrite, smithsonite, hemimorphite A botryoidal (/ˌbɒtriˈɔɪdəl/ BOT-ree-OY-dəl) texture or mineral habit, is one in which the mineral has an external form composed of many rounded segments, named for the Ancient Greek βότρυς (bótrus), meaning “a bunch of grapes“.… Read more.
-
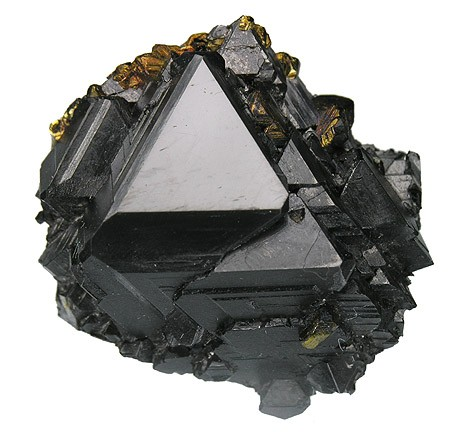
Tetrahedral – Tetrahedron-shaped, triangular pyramid (four-sided)
Common examples include: tetrahedrite, spinel, sphalerite, magnetite Read more.
-
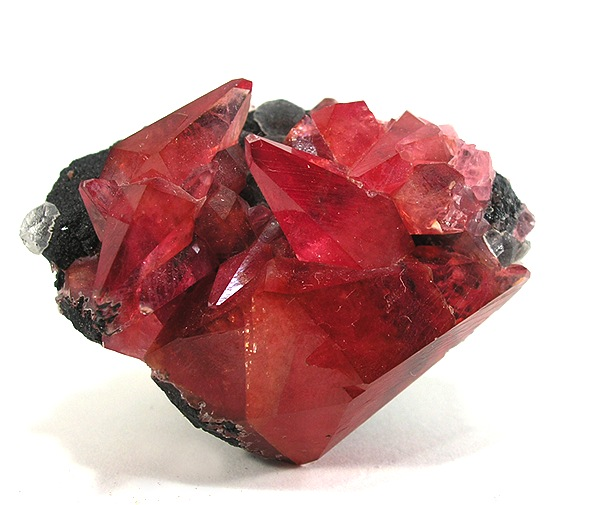
Scalenohedral – Scalenohedron-shaped, pointy ends
Common examples include: calcite, rhodochrosite, titanite In crystallography, “regular” right “symmetric” “didigonal” (8-faced) and ditrigonal (12-faced) scalenohedra exist. The smallest geometric scalenohedra have eight faces, and are topologically identical to the regular octahedron. In… Read more.
-
Rhombohedral – Rhombohedron-shaped (six-faced rhombi)
Common examples include: calcite, rhodochrosite, siderite Read more.
-
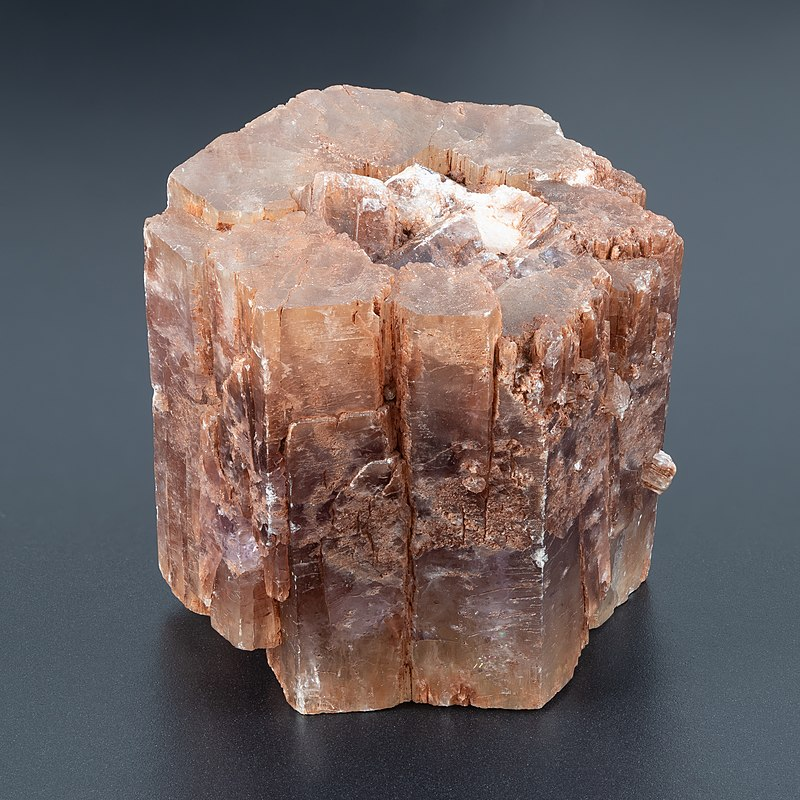
Pseudo-hexagonal – Hexagon-like appearance due to cyclic twinning
Common examples include: aragonite, chrysoberyl Read more.
-
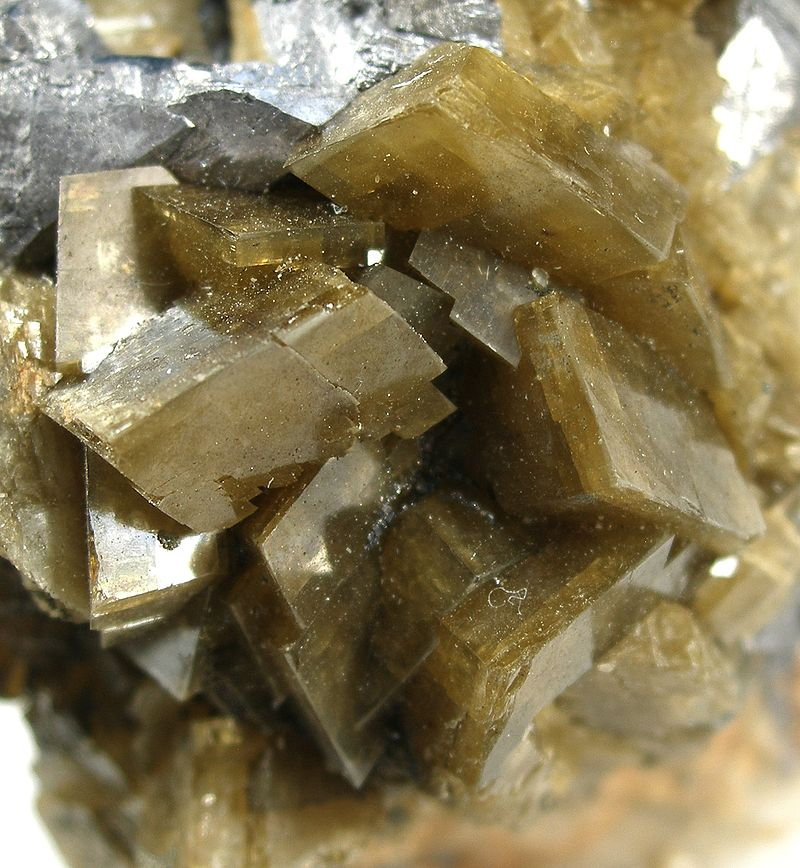
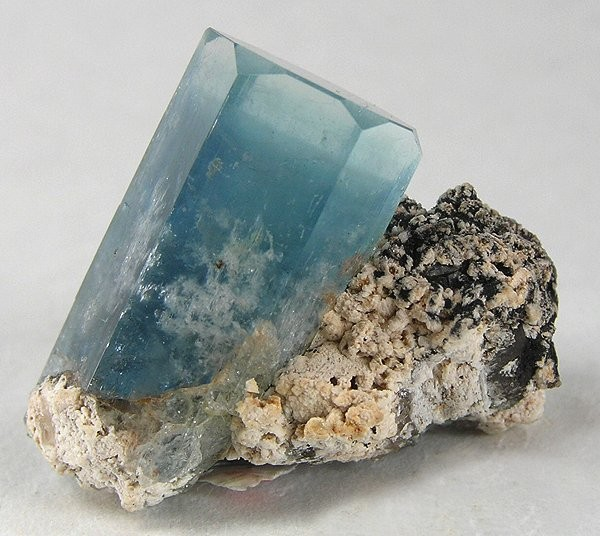
Prismatic – Elongate, prism-like: well-developed crystal faces parallel to the vertical axis
Common examples include: beryl, tourmaline, vanadinite, emerald Read more.