Microbiology
-
Thermolysin – The Tiny Terminator of Plasma Proteins!
Both thermolysin and snake venom metalloproteinases (SVMPs) share a similar mechanism of action, utilizing zinc ions to hydrolyze peptide bonds in proteins Read more.
-
Subtilisin
Subtilisin is a protease (a protein-digesting enzyme) initially obtained from Bacillus subtilis. Subtilisins belong to subtilases, a group of serine proteases that – like all serine proteases – initiate the nucleophilic attack on the peptide (amide) bond through a serine residue at the active site. Subtilisins… Read more.
-
Proprotein convertases (PPCs) are a family of proteins that activate other proteins
Many proteins are inactive when they are first synthesized, because they contain chains of amino acids that block their activity. Proprotein convertases remove those chains and activate the protein. The… Read more.
-
The Two-Faced Troublemaker: Bacillus cereus, the Jekyll and Hyde of Bacteria
Bacillus cereus is the bacterial world’s very own shape-shifting supervillain! This microscopic menace is the master of disguise, equally at home in your garden soil as it is crashing your… Read more.
-
Bacillus thuringiensis: the James Bond of biological pest control
In the microscopic world of bacteria, Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), a gram-positive, soil-dwelling microbe is the go-to secret agent for farmers and gardeners worldwide, thanks to its uncanny ability to produce… Read more.
·
-
Perivitellins are egg proteins found in the perivitelline fluid of many gastropods
Perivitellins are multifunctional complexes providing the developing embryo with nutrition, protection from the environment, and defense against predators. Despite the central role perivitellins play in reproduction and development, there is… Read more.
·
-
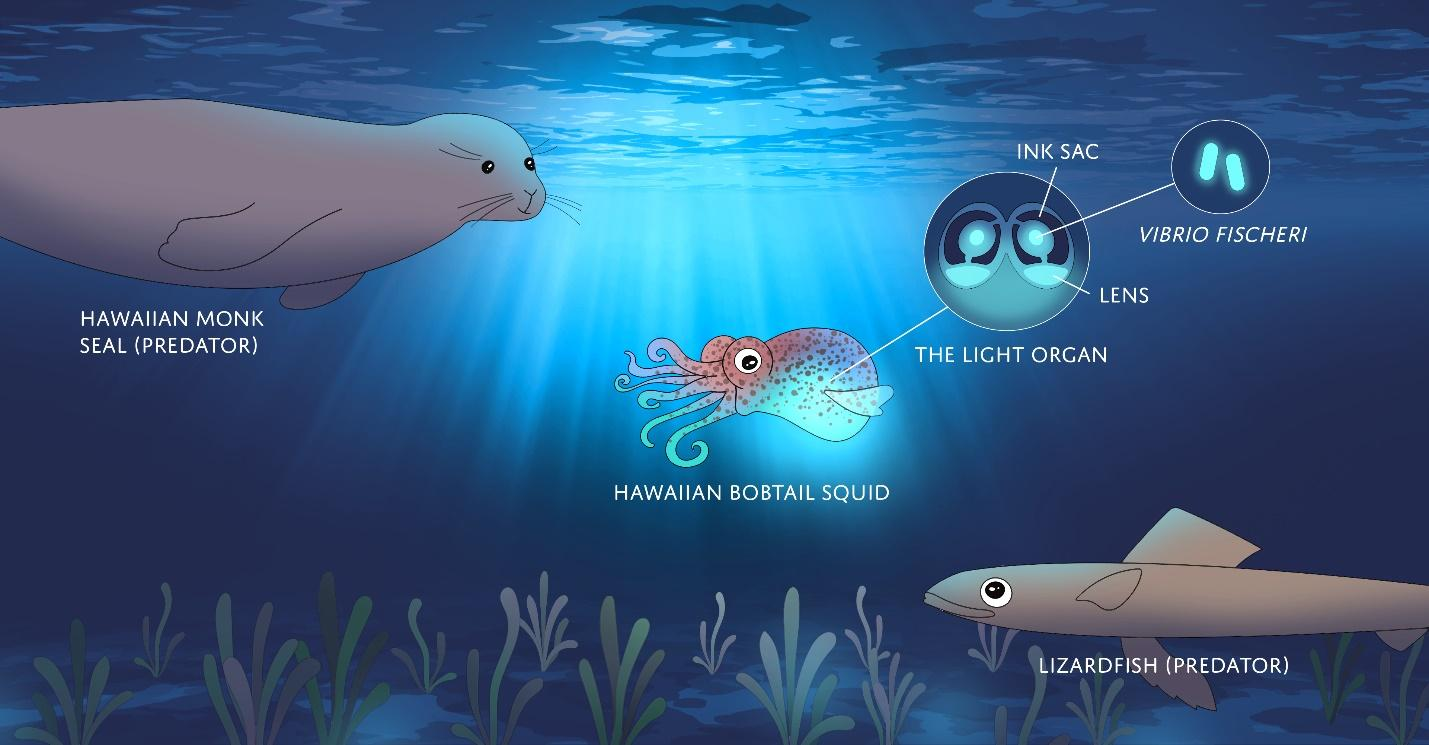
Aliivibrio fischeri (aka Vibrio fischeri), a bioluminescent bacteria and a glowing squid
Aliivibrio fischeri (also called Vibrio fischeri) is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium found globally in marine environments. This species has bioluminescent properties, and is found predominantly in symbiosis with various marine animals, such as the Hawaiian bobtail squid. It is heterotrophic, oxidase-positive, and motile by means of a… Read more.
-
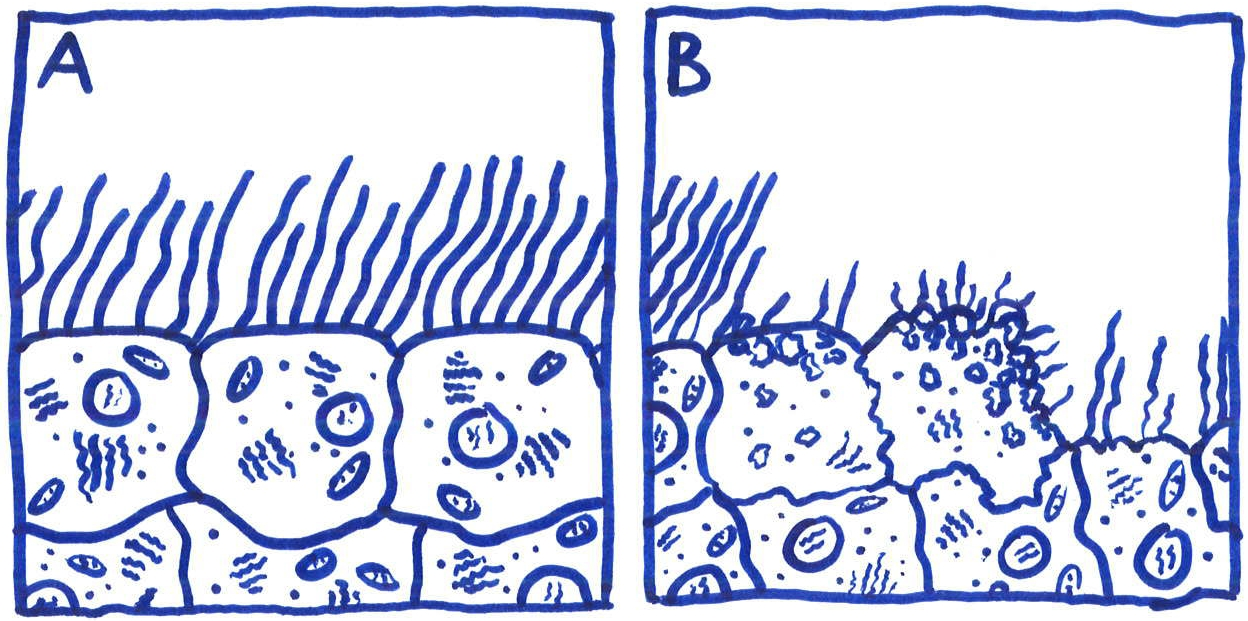
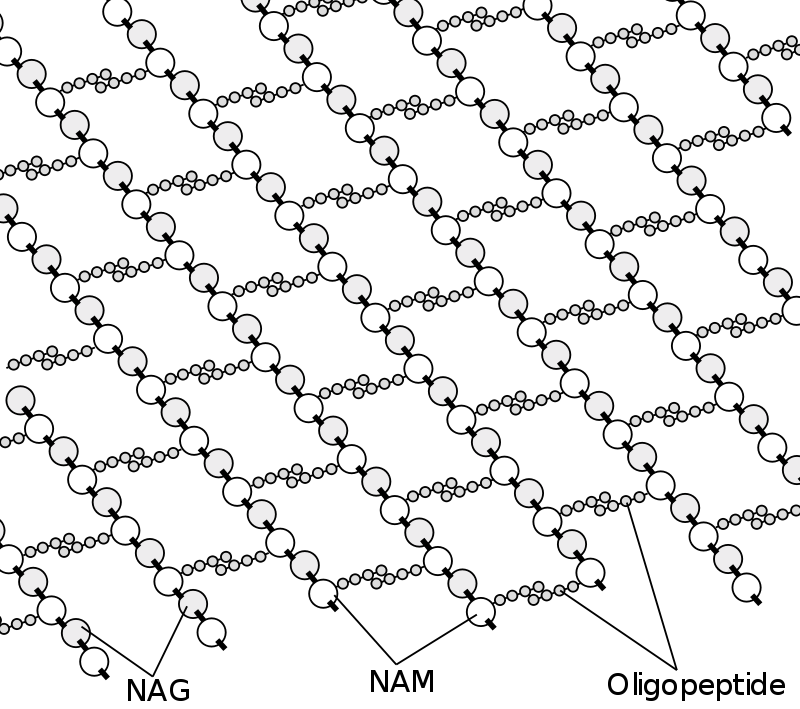
Tracheal cytotoxin (TCT) is a soluble piece of peptidoglycan (PGN) found in the cell wall of all gram-negative bacteria, but only some bacteria species release TCT including Bordetella pertussis, Vibrio fischeri, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Tracheal cytotoxin (TCT) is a 921 dalton glycopeptide released by Bordetella pertussis, Vibrio fischeri (as a symbiosis chemical), and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (among other peptidoglycan-derived cytotoxins it produces). It is a soluble piece of peptidoglycan (PGN) found in the cell wall of all gram-negative bacteria, but only some bacteria species… Read more.
-
Streptomyces is the largest antibiotic-producing genus, producing antibacterial, antifungal, and antiparasitic drugs, and also a wide range of other bioactive compounds, such as immunosuppressants.
Streptomyces is the largest genus of Actinomycetota, and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 700 species of Streptomyces bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have very large genomes with high GC content. Found predominantly in soil… Read more.