Tag: BACTERIA
-

Thermolysin – The Tiny Terminator of Plasma Proteins!
Both thermolysin and snake venom metalloproteinases (SVMPs) share a similar mechanism of action, utilizing zinc ions to hydrolyze peptide bonds in proteins
-
Dermatan sulfate (and a few other things)
Dermatan sulfate is a glycosaminoglycan (formerly called a mucopolysaccharide) found mostly in skin, but also in blood vessels, heart valves, tendons, and lungs. It is also referred to as chondroitin sulfate B, although it is no longer classified as a form of chondroitin sulfate by most sources. The formula is C14H21NO15S. This carbohydrate is composed of linear polymers of disaccharide units that contain, N-acetyl galactosamine (GalNAc) and iduronic…
-
Perivitellins are egg proteins found in the perivitelline fluid of many gastropods
Perivitellins are multifunctional complexes providing the developing embryo with nutrition, protection from the environment, and defense against predators. Despite the central role perivitellins play in reproduction and development, there is little information about their role in gastropod Molluscs. Most studies of perivitellins have been performed in eggs of Ampullaridae, a family of freshwater snails (Caenogastropoda), notably the Pomacea genus, mostly…
-
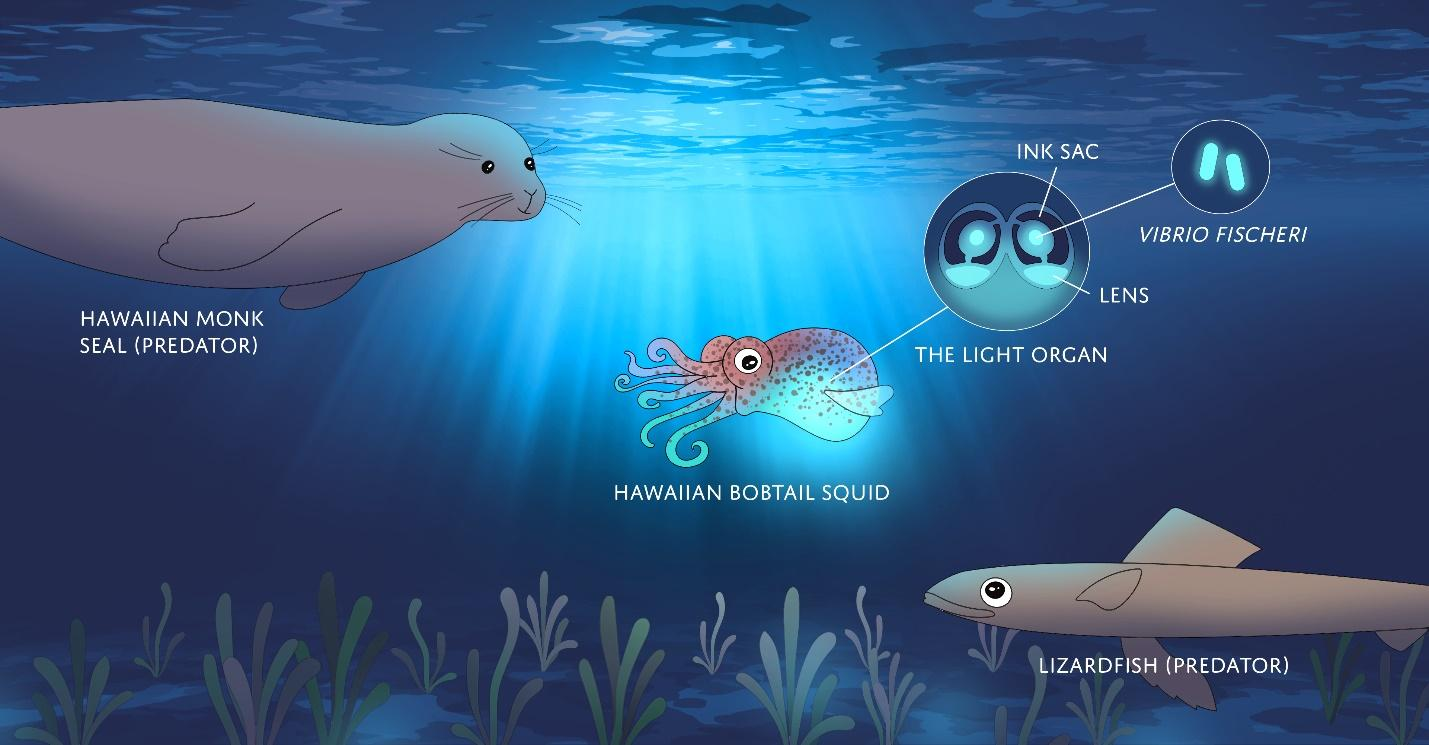

Aliivibrio fischeri (aka Vibrio fischeri), a bioluminescent bacteria and a glowing squid
Aliivibrio fischeri (also called Vibrio fischeri) is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium found globally in marine environments. This species has bioluminescent properties, and is found predominantly in symbiosis with various marine animals, such as the Hawaiian bobtail squid. It is heterotrophic, oxidase-positive, and motile by means of a single polar flagella. Free-living A. fischeri cells survive on decaying organic matter. The bacterium is a key research organism for examination of microbial bioluminescence, quorum sensing, and bacterial-animal symbiosis. It is named…
-
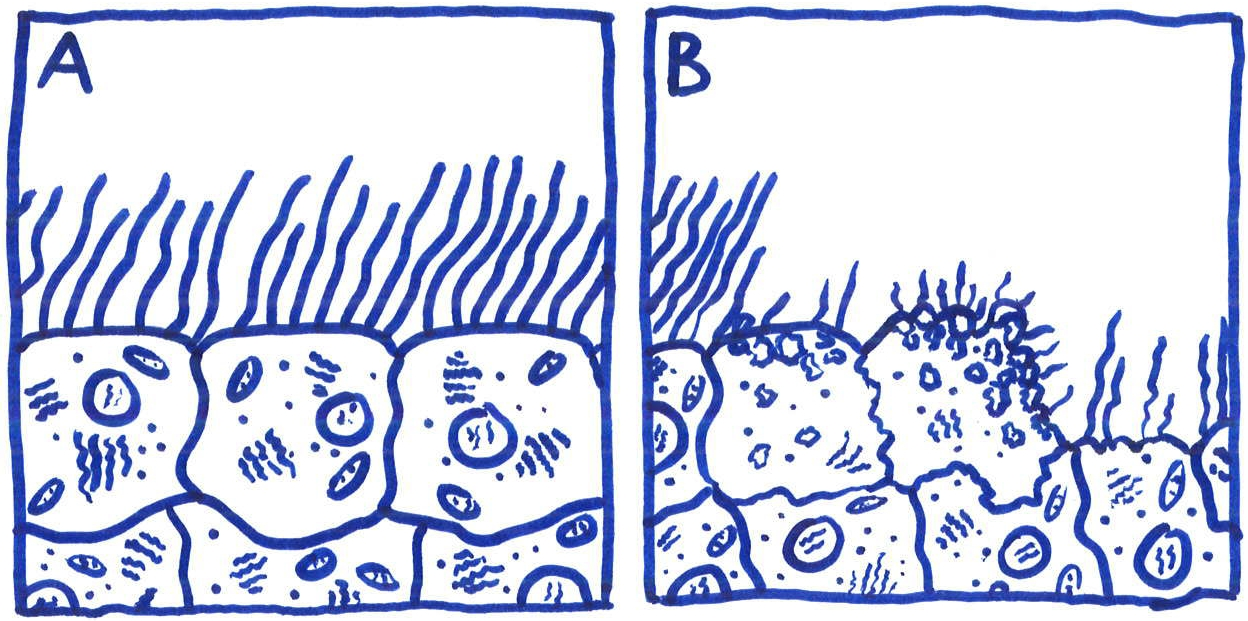
Tracheal cytotoxin (TCT) is a soluble piece of peptidoglycan (PGN) found in the cell wall of all gram-negative bacteria, but only some bacteria species release TCT including Bordetella pertussis, Vibrio fischeri, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Tracheal cytotoxin (TCT) is a 921 dalton glycopeptide released by Bordetella pertussis, Vibrio fischeri (as a symbiosis chemical), and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (among other peptidoglycan-derived cytotoxins it produces). It is a soluble piece of peptidoglycan (PGN) found in the cell wall of all gram-negative bacteria, but only some bacteria species release TCT due to inability to recycle this piece of anhydromuropeptide. History In 1980, it was discovered that B. pertussis could attach to hamster tracheal epithelial (HTE) cells, and also, that…
-

Streptomyces is the largest antibiotic-producing genus, producing antibacterial, antifungal, and antiparasitic drugs, and also a wide range of other bioactive compounds, such as immunosuppressants.
Streptomyces is the largest genus of Actinomycetota, and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 700 species of Streptomyces bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have very large genomes with high GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct “earthy” odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin. Different strains of the…
-

Cryptanaerobacter phenolicus transforms phenol into benzoate via 4-hydroxybenzoate
Benzoic acid occurs naturally in many plants and serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of many secondary metabolites. Salts of benzoic acid are used as food preservatives. Benzoic acid is an important precursor for the industrial synthesis of many other organic substances. The salts and esters of benzoic acid are known as benzoates. Benzoic acid occurs naturally as do its esters in many plant…
-
Rhodococcus phenolicus is a bacterium able to degrade phenol as sole carbon source
Rhodococcus phenolicus is a bacterium species in the genus Rhodococcus. Phenolicus comes from New Latin noun phenol –olis, phenol; Latin masculine gender suff. –icus, suffix used in adjectives with the sense of belonging to; New Latin masculine gender adjective phenolicus, belonging to phenol. This species is able to degrade phenol as sole carbon source. External links Categories:
-
Xylose is the first saccharide added to the serine or threonine in the proteoglycan type O-glycosylation
Xylose is the first saccharide added to the serine or threonine in the proteoglycan type O-glycosylation, and, so, it is the first saccharide in biosynthetic pathways of most anionic polysaccharides such as heparan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate. Definitions Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a “core protein” with one or more covalently attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The point of attachment is a serine (Ser) residue to which the glycosaminoglycan is joined through…
-
Carbonic anhydrases (or carbonate dehydratases) and inhibitors
The carbonic anhydrases (or carbonate dehydratases) (EC 4.2.1.1) form a family of enzymes that catalyze the interconversion between carbon dioxide and water and the dissociated ions of carbonic acid (i.e. bicarbonate and hydrogen ions). The active site of most carbonic anhydrases contains a zinc ion. They are therefore classified as metalloenzymes. The enzyme maintains acid-base balance and helps transport carbon dioxide. Carbonic anhydrase helps maintain acid–base homeostasis, regulate pH, and fluid balance. Depending on its location, the role of the enzyme changes slightly. For…
-
Production of Carminic Acid by Metabolically Engineered Escherichia coli
Production of Carminic Acid by Metabolically Engineered Escherichia coliDongsoo Yang, Woo Dae Jang, and Sang Yup Lee Journal of the American Chemical Society 2021 143 (14), 5364-5377 DOI: 10.1021/jacs.0c12406 Abstract: Carminic acid is an aromatic polyketide found in scale insects (i.e., Dactylopius coccus) and is a widely used natural red colorant. It has long been produced…
-
What Is A Siderophore?
Siderophores (Greek: "iron carrier") are small, high-affinity iron-chelating compounds that are secreted by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. They help the organism accumulate iron. Although a widening range of siderophore functions is now being appreciated. Siderophores are among the strongest (highest affinity) Fe3+ binding agents known. Phytosiderophores are siderophores produced by plants.
-

Delftia acidovorans
Delftia acidovorans is a Gram-negative, motile, non-sporulating, rod-shaped bacterium known for its ability to biomineralize gold and bioremediation characteristics.
-

Cupriavidus metallidurans
C. metallidurans plays a vital role, together with Delftia acidovorans, in the formation of gold nuggets. It precipitates metallic gold from a solution of gold(III) chloride, a compound highly toxic to most other microorganisms.
-
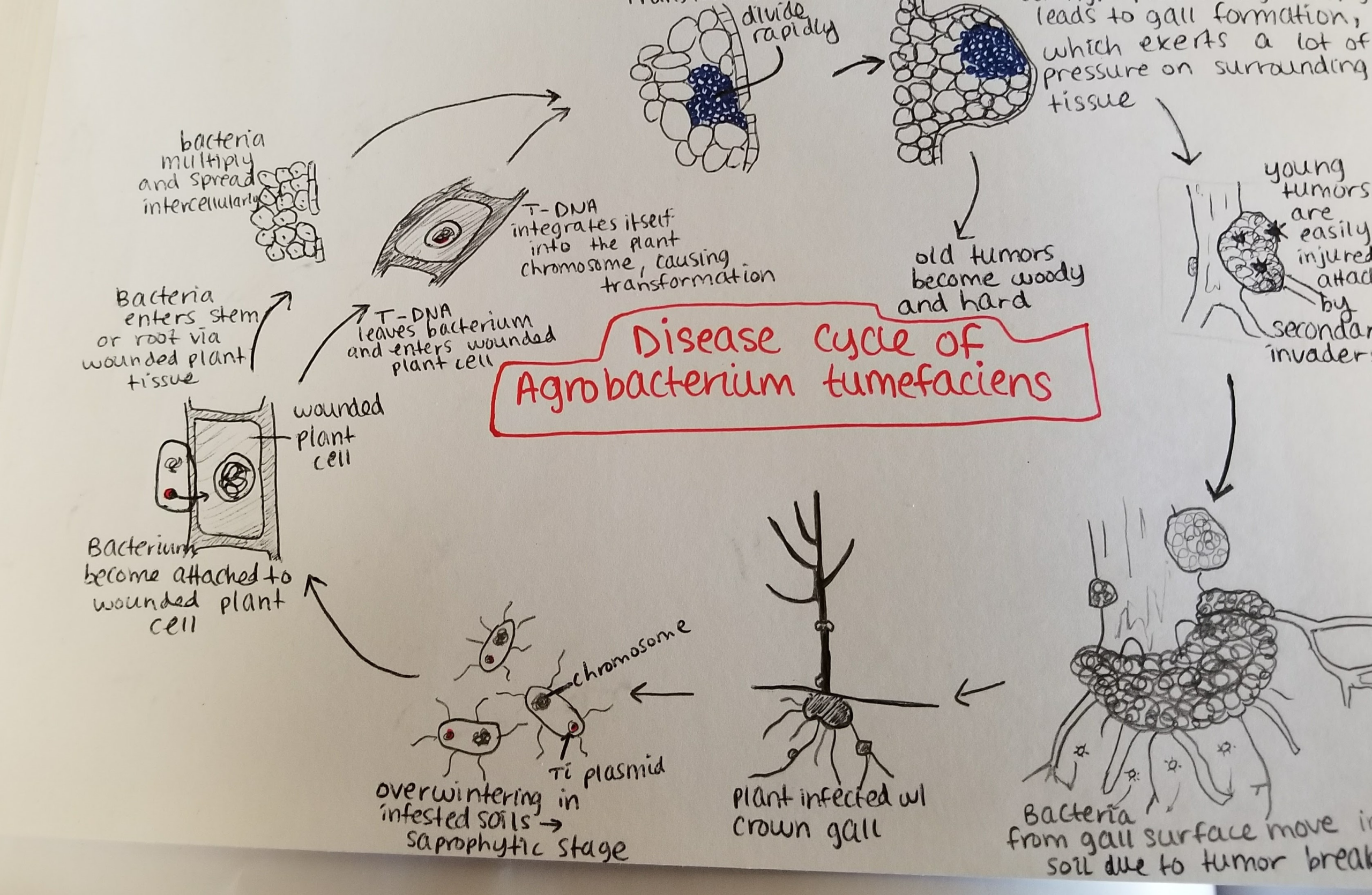
Bacterial diseases of hazelnut (Corylus avellana & Corylus spp.) and more
Bacterial blight Xanthomonas arboricola Scientific classification Domain: Bacteria Phylum: Pseudomonadota Class: Gammaproteobacteria Order: Xanthomonadales Family: Xanthomonadaceae Genus: Xanthomonas Species: X. arboricola Binomial name Xanthomonas arboricolaVauterin et al. 1995 Type strain ATCC 49083 Xanthomonas arboricola pv. corylina Xanthomonas arboricola is a species of bacteria. This phytopathogenic bacterium can cause disease in trees like Prunus, hazelnut and walnut. Hosts and symptoms Xanthomonas arboricola has a vast host range, however,…
NOTES
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc


