Tag: Neurological
-
DMT1 aka DCT1 and NRAMP2
Natural resistance-associated macrophage protein 2 (NRAMP 2), also known as divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) and divalent cation transporter 1 (DCT1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC11A2 (solute carrier family 11, member 2) gene. DMT1 represents a large family of orthologous metal ion transporter proteins that are highly conserved from bacteria to humans. As its name suggests, DMT1 binds a variety of divalent metals…
-
Tobacco-derived 4R-cembranoid protects neuronal cells from oxygen-glucose deprivation by modulating microglial cell activation
Fu, Hefei et al. “4R-cembranoid protects neuronal cells from oxygen-glucose deprivation by modulating microglial cell activation.” Brain research bulletin vol. 179 (2022): 74-82. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2021.12.007 In the search for novel compounds to treat neurodegenerative diseases, we found that 4R-cembranoid, an extract from tobacco leaves, may be a lead compound with anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. 4R belongs to the…
-

Patent for protecting and treating organophosphate-induced neuronal injury with tobacco-derived cembranoids and analogues
Ford, Byron, Ferchmin Peter, Eterovic, Vesna, Methods and compositions for protecting and treating neuroinjury (Patent), United States Grant US-8530525-B2 Assignee: Central University of the Caribbean, Morehouse School of Medicine, Status: Active, Expires 2031-05-19, Document history 2013-09-10 Publication date, 2010-07-01 Filing date, 2009-07-14 Priority date. Funded by National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institute on Minority Health and…
-
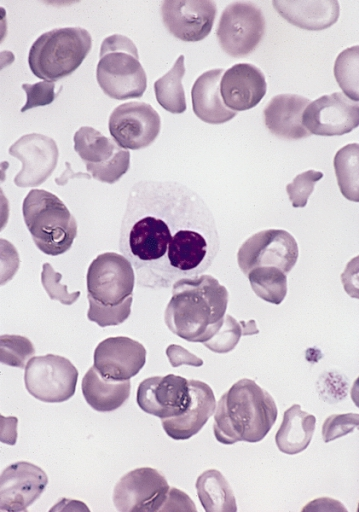
Pelger–Huët anomaly, congenital and acquired, also pince-nez, laminopathy and a little ebola
Pelger–Huët anomaly is a blood laminopathy associated with the lamin B receptor, wherein several types of white blood cells (neutrophils and eosinophils) have nuclei with unusual shape (being bilobed, peanut or dumbbell-shaped instead of the normal trilobed shape) and unusual structure (coarse and lumpy). It is a genetic disorder with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Heterozygotes are clinically normal, although their neutrophils may be mistaken for immature cells which may cause…
-

A Mad Scientist’s Dream – Rumpless Chickens (and more)
Today, we delve into the bizarre phenomenon of rumpless chickens—a feathered marvel characterized by caudal dysplasia, or as some like to call it, the ultimate chicken makeover! These quirky birds are missing their pygostyle, that charming little appendage known as the “parson’s nose,” a mutation that defies nature itself. This peculiar trait is inherited through…
-

Deficiency of Adenosine deaminase 2 (DADA2)
Deficiency of Adenosine deaminase 2 (DADA2) is a monogenic disease associated with systemic inflammation and vasculopathy that affects a wide variety of organs in different patients. As a result, it is hard to characterize a patient with this disorder. Manifestations of the disease include but are not limited to recurrent fever, livedoid rash (reticularis or racemosa), various cytopenias, stroke, immunodeficiency, and bone marrow failure. Symptoms often onset during…
-

Aetokthonotoxin (AETX) aka ‘eagle toxin’ discovered in 2021
Aetokthonotoxin (AETX), colloquially ‘eagle toxin’, was discovered in 2021 as the cyanobacterial neurotoxin causing vacuolar myelinopathy (VM) in eagles in North America. Avian vacuolar myelinopathy (AVM) is a fatal neurological disease that affects various waterbirds and raptors. It is most common in the bald eagle and American coot, and it is known in the killdeer, bufflehead, northern shoveler, American wigeon, Canada goose, great horned owl, mallard, and ring-necked duck. Avian vacuolar myelinopathy is a newly discovered disease that…
-
In mouse models of Alzheimer’s Disease, it has been shown that there is a decrease in neuronal histone acetylation, a critical function of CBP
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease whose pathology is diagnosed based on the presence of neuritic amyloid beta (Aβ) plaques and neurofibrillary tau (τ) tangles. Because the exact causes of the disease are not clearly understood, there are a number of different mechanisms by which CBP (CREB-binding protein) is hypothesized to play a role…
-
Diminished CBP activity and decreased neuronal histone acetylation is associated with Huntington’s Disease
Huntington’s Disease (HD) is a fatal, progressing neurodegenerative disorder that is the result of a genetic mutation in the Huntingtin gene causing synthesis of a mutated huntingtin (Htt) protein. Symptoms most frequently associated with this disease are movement disorders, including impaired motor function, behavioral modification and cognitive impairment that ultimately results in dementia. It has been observed in animal…
-
Decreased concentrations of CBP and lower amounts of H3 and H4 acetylation associated with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD) is a classification of diseases that all result from alcohol exposure during pregnancy. Symptoms of these disorders include poor cerebellar-dependent learning, motor coordination and impaired balance. In rats with FASD, it was shown that they had decreased concentrations of CBP and lower amounts of H3 and H4 acetylation.
-
CREB has been shown to have neuroprotective properties
Because of its association with CBP, understanding the role of CBP in neurological pathways and how aberrations influence disease is becoming of increasing interest. Numerous animal models have been designed in order to evaluate changes in motor, learning and memory function in mice with CBP mutations. Conditional knockout (cKO) mice that were hemizygous for CBP…
NOTES
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc

