Tag: Protein
-
Albumen prints and egg whites…all the rage back in the day…and a few other things
The albumen print, also called albumen silver print, was published in January 1847 by Louis Désiré Blanquart-Evrard, and was the first commercially exploitable method of producing a photographic print on a paper base from a negative. It used the albumen found in egg whites to bind the photographic chemicals to the paper and became the dominant form of photographic positives from 1855 to the start…
-
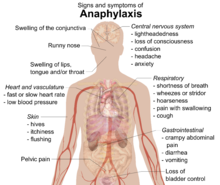
Von Willebrand factor (VWF) is a large multimeric glycoprotein present in blood plasma and produced constitutively as ultra-large VWF in endothelium (in the Weibel–Palade bodies), megakaryocytes (α-granules of platelets), and subendothelial connective tissue
Von Willebrand factor (VWF) is a blood glycoprotein that promotes hemostasis, specifically, platelet adhesion. It is deficient and/or defective in von Willebrand disease and is involved in many other diseases, including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, Heyde’s syndrome, and possibly hemolytic–uremic syndrome. Increased plasma levels in many cardiovascular, neoplastic, metabolic (e.g. diabetes), and connective tissue diseases are presumed to arise from adverse changes to the endothelium, and may predict an increased…
-
Ectodomain Shedding & Sheddases & a whole bunch of Adams
An ectodomain is the domain of a membrane protein that extends into the extracellular space (the space outside a cell). Ectodomains are usually the parts of proteins that initiate contact with surfaces, which leads to signal transduction. A notable example of an ectodomain is the S protein, commonly known as the spike protein, of the viral particle responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The ectodomain region of the…
-

Ceruloplasmin carries more than 95% of the total copper in healthy human plasma and in addition plays a role in iron metabolism. It was first described in 1948.
Ceruloplasmin (or caeruloplasmin) is a ferroxidase enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CP gene. Ceruloplasmin is the major copper-carrying protein in the blood, and in addition plays a role in iron metabolism. It was first described in 1948. Another protein, hephaestin, is noted for its homology to ceruloplasmin, and also participates in iron and probably copper metabolism. Function Ceruloplasmin (CP) is an enzyme (EC 1.16.3.1) synthesized…
-
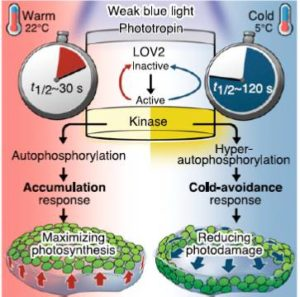
Phototropins are part of the phototropic sensory system in plants that causes various environmental responses in plants
Phototropins are photoreceptor proteins (more specifically, flavoproteins) that mediate phototropism responses in various species of algae, fungi and higher plants. Note: Flavoproteins are proteins that contain a nucleic acid derivative of riboflavin. These proteins are involved in a wide array of biological processes, including removal of radicals contributing to oxidative stress, photosynthesis, and DNA repair. The flavoproteins are some of the most-studied families of enzymes. Flavoproteins have either FMN (flavin mononucleotide) or FAD…
-
Proline and a few other notes
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group -NH2 but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the protonated form (NH2+) under biological conditions, while the carboxyl group is in the deprotonated −COO− form. The “side chain” from the α carbon connects to the nitrogen forming a pyrrolidine loop, classifying it…
-

Pterion and Pteron Notes
The pterion is the region where the frontal, parietal, temporal, and sphenoid bones join. It is located on the side of the skull, just behind the temple. Structure The pterion is located in the temporal fossa, approximately 2.6 cm behind and 1.3 cm above the posterolateral margin of the frontozygomatic suture. It is the junction between four bones: These bones are typically joined by five cranial sutures: Clinical significance Haematoma…
-
Xylose is the first saccharide added to the serine or threonine in the proteoglycan type O-glycosylation
Xylose is the first saccharide added to the serine or threonine in the proteoglycan type O-glycosylation, and, so, it is the first saccharide in biosynthetic pathways of most anionic polysaccharides such as heparan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate. Definitions Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a “core protein” with one or more covalently attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The point of attachment is a serine (Ser) residue to which the glycosaminoglycan is joined through…
-
Carboxypeptidases function in blood clotting, growth factor production, wound healing, reproduction, and many other processes
A carboxypeptidase (EC number 3.4.16 – 3.4.18) is a protease enzyme that hydrolyzes (cleaves) a peptide bond at the carboxy-terminal (C-terminal) end of a protein or peptide. This is in contrast to an aminopeptidases, which cleave peptide bonds at the N-terminus of proteins. Humans, animals, bacteria and plants contain several types of carboxypeptidases that have diverse functions ranging from catabolism to protein maturation. At least two mechanisms have been discussed. Functions Initial studies…
-
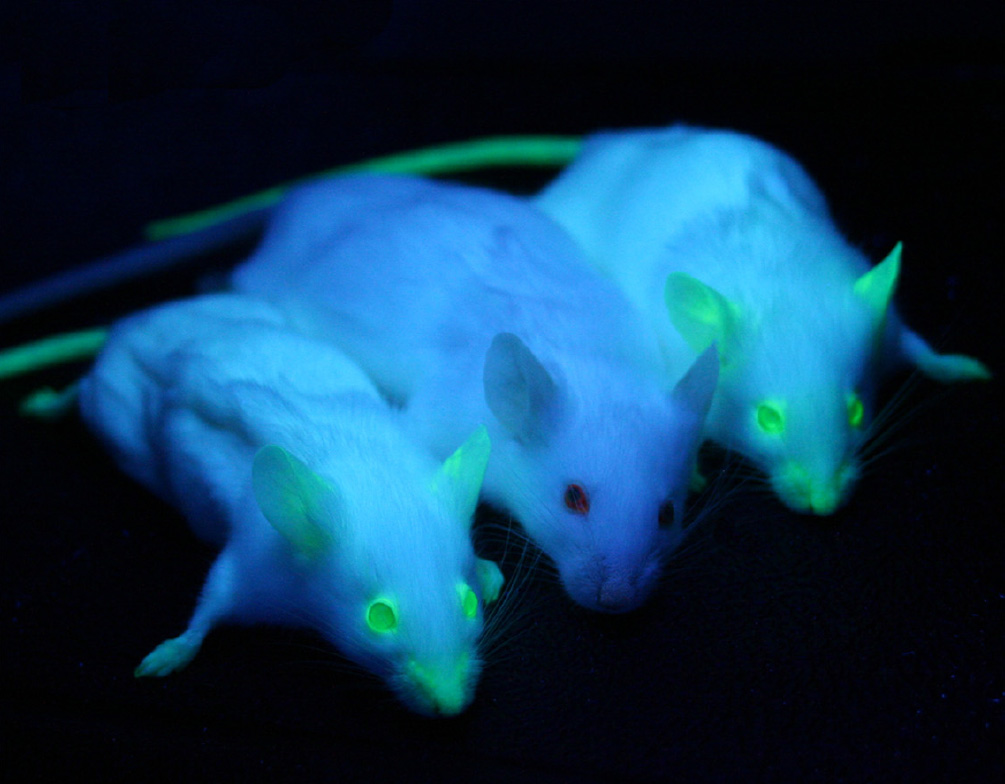

Green fluorescent protein (GFP)
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits bright green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. Prendergast FG, Mann KG (Aug 1978). “Chemical and physical properties of aequorin and the green fluorescent protein isolated from Aequorea forskålea”. Biochemistry. 17 (17): 3448–53. doi:10.1021/bi00610a004. PMID 28749. Tsien RY (1998). “The green fluorescent protein” (PDF). Annual Review of Biochemistry. 67: 509–44. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.509. PMID 9759496 The label GFP traditionally refers to the protein first isolated…
-
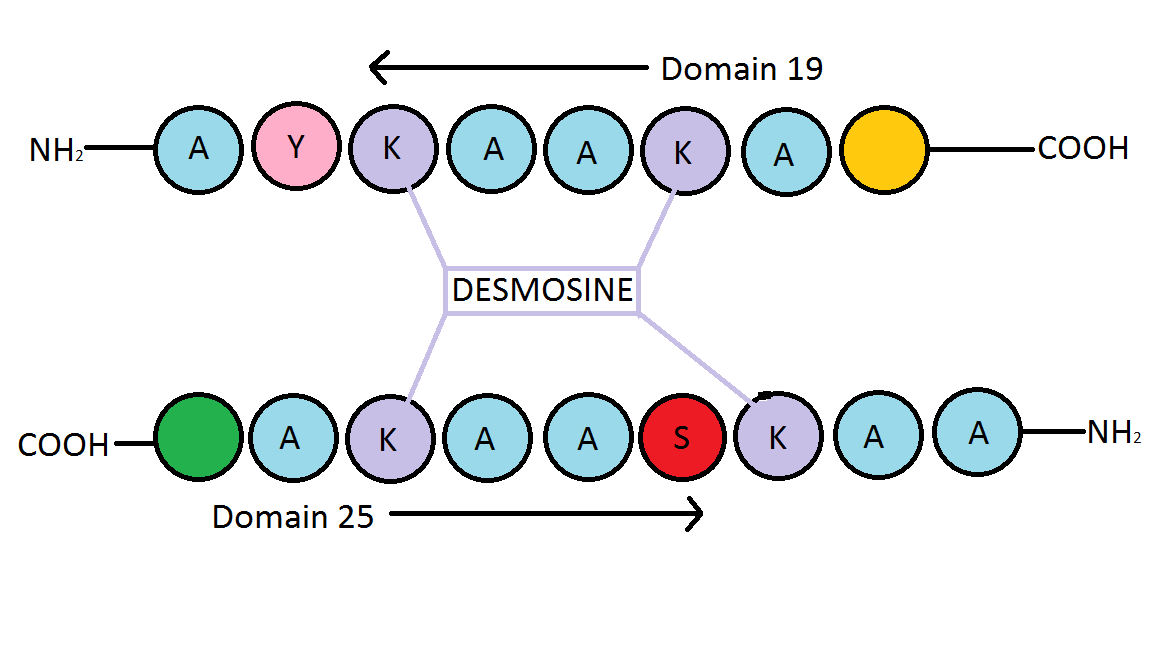
Desmosine
Desmosine is an amino acid found uniquely in elastin, a protein found in connective tissue such as skin, lungs, and elastic arteries. Desmosine is a component of elastin and cross links with its isomer, isodesmosine, giving elasticity to the tissue. Detection of desmosine in urine, plasma or sputum samples can be a marker for elastin breakdown due to high elastase activity related to certain diseases.…
-
Brain natriuretic peptide 32 (BNP)
Brain natriuretic peptide 32 (BNP), also known as B-type natriuretic peptide, is a hormone secreted by cardiomyocytes in the heart ventricles in response to stretching caused by increased ventricular blood volume. BNP is one of two natriuretic peptides “UniProt”. www.uniprot.org. Retrieved 11 August 2022. The 32-amino acid polypeptide BNP is secreted attached to a 76–amino acid N-terminal fragment in the prohormone called NT-proBNP (BNPT), which is biologically inactive. Once released, BNP binds…
-
Triiodothyronine, aka T3
Triiodothyronine, also known as T3, is a thyroid hormone. It affects almost every physiological process in the body, including growth and development, metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate. Bowen, R. (2010-07-24). “Physiologic Effects of Thyroid Hormones”. Colorado State University. Retrieved 2013-09-29. Production of T3 and its prohormone thyroxine (T4) is activated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is released from the anterior pituitary gland. This pathway is part of a closed-loop feedback process: Elevated…
-
Kaede (protein)
Kaede is a photoactivatable fluorescent protein naturally originated from a stony coral, Trachyphyllia geoffroyi. Its name means “maple” in Japanese. With the irradiation of ultraviolet light (350–400 nm), Kaede undergoes irreversible photoconversion from green fluorescence to red fluorescence. Kaede is a homotetrameric protein with the size of 116 kDa. The tetrameric structure was deduced as its primary structure is only 28 kDa. This tetramerization possibly makes Kaede have a low tendency to…
NOTES
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc

