Tag: zinc
-

Sterol carrier proteins (aka nonspecific lipid transfer proteins)
These proteins are different from plant nonspecific lipid transfer proteins but structurally similar to small proteins of unknown function from Thermus thermophilus. This domain is involved in binding sterols. The human sterol carrier protein 2 (SCP2) is a basic protein that is believed to participate in the intracellular transport of cholesterol and various other lipids. Human…
-

Glucuronic acid is a uronic acid that was first isolated from urine
Glucuronic acid (from Greek γλεῦκος “wine, must” and οὖρον “urine“) is a uronic acid that was first isolated from urine (hence the name”uronic acid”). It is found in many gums such as gum arabic (approx. 18%), xanthan, and kombucha tea and is important for the metabolism of microorganisms, plants and animals. Not to be confused with Gluconic acid (Gluconic acid occurs naturally in fruit, honey, and wine. As a food additive E574, it is now known as an acidity regulator.…
-
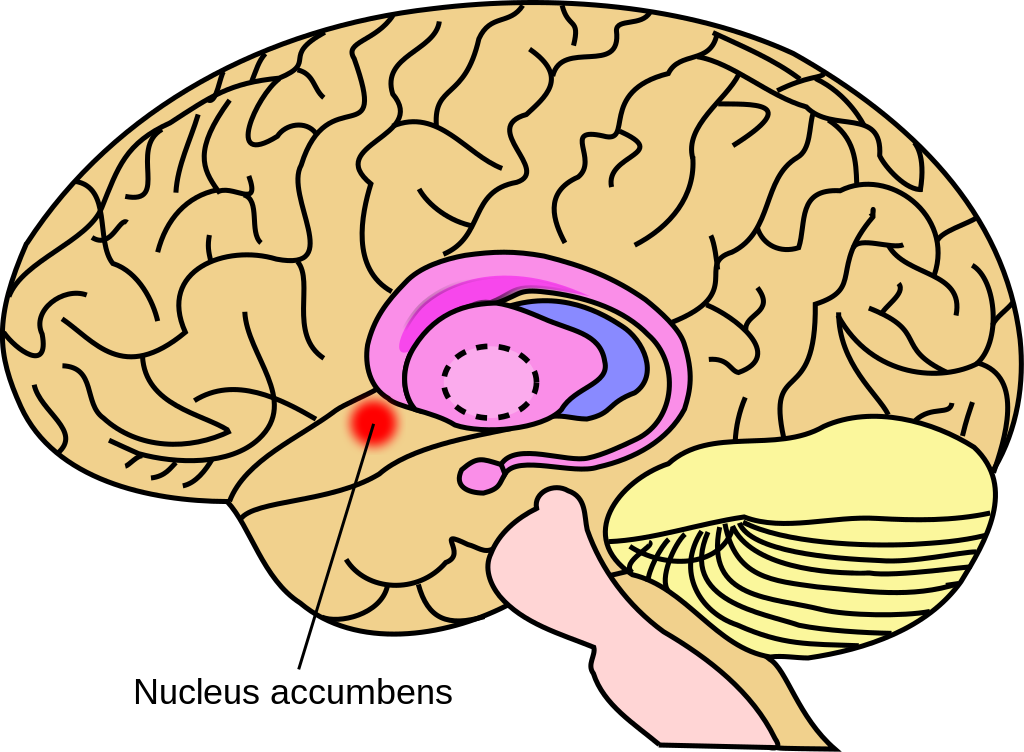
Nucleus accumbens aka accumbens nucleus
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the nucleus accumbens septi, Latin for “nucleus adjacent to the septum“) is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypothalamus. The nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle collectively form the ventral striatum. The ventral striatum and dorsal striatum collectively form the striatum, which is the main component of the basal ganglia. The dopaminergic neurons of the mesolimbic pathway project onto the GABAergic medium…
-

Memento mori (symbolic trope)
Memento mori (Latin for ‘remember that you [have to] die’) is an artistic or symbolic trope acting as a reminder of the inevitability of death. The concept has its roots in the philosophers of classical antiquity and Christianity, and appeared in funerary art and architecture from the medieval period onwards. The most common motif is a skull, often accompanied by one or more bones. Often this alone is…
-
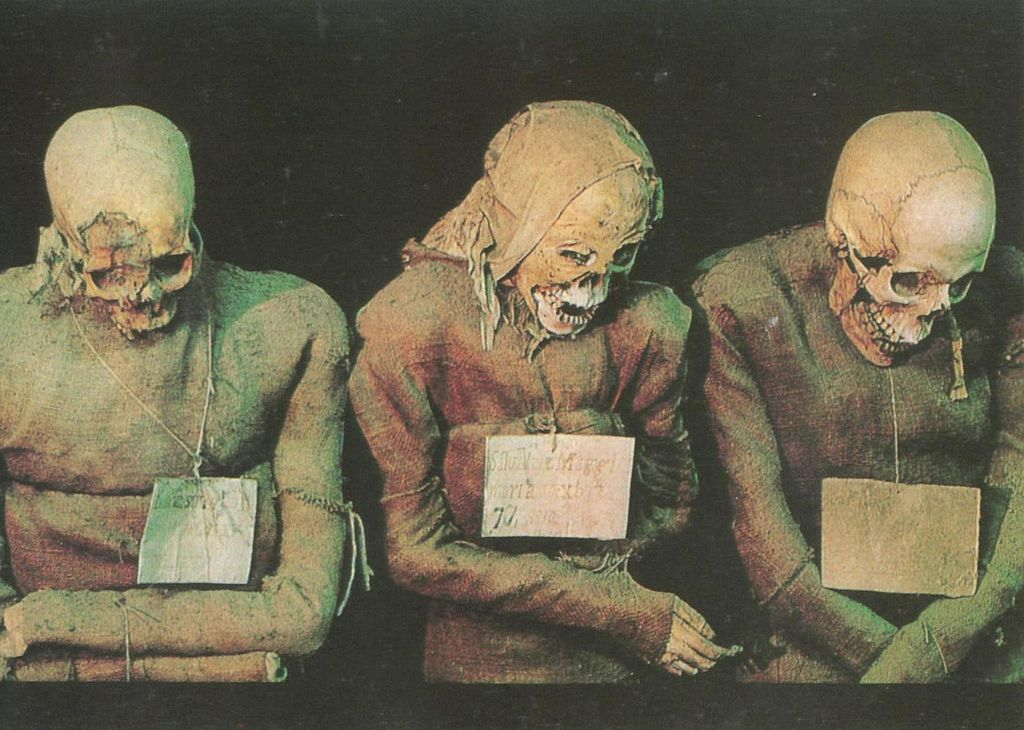

The Capuchin Catacombs of Palermo
The Capuchin Catacombs of Palermo (also Catacombe dei Cappuccini or Catacombs of the Capuchins) are burial catacombs in Palermo, Sicily, southern Italy. Today they provide a somewhat macabre tourist attraction as well as an extraordinary historical record. Historical background Palermo’s Capuchin monastery outgrew its original cemetery in the 16th century and monks began to excavate crypts below it. In 1599 they mummified one of their number, the recently-deceased brother Silvestro of Gubbio, and placed him…
-
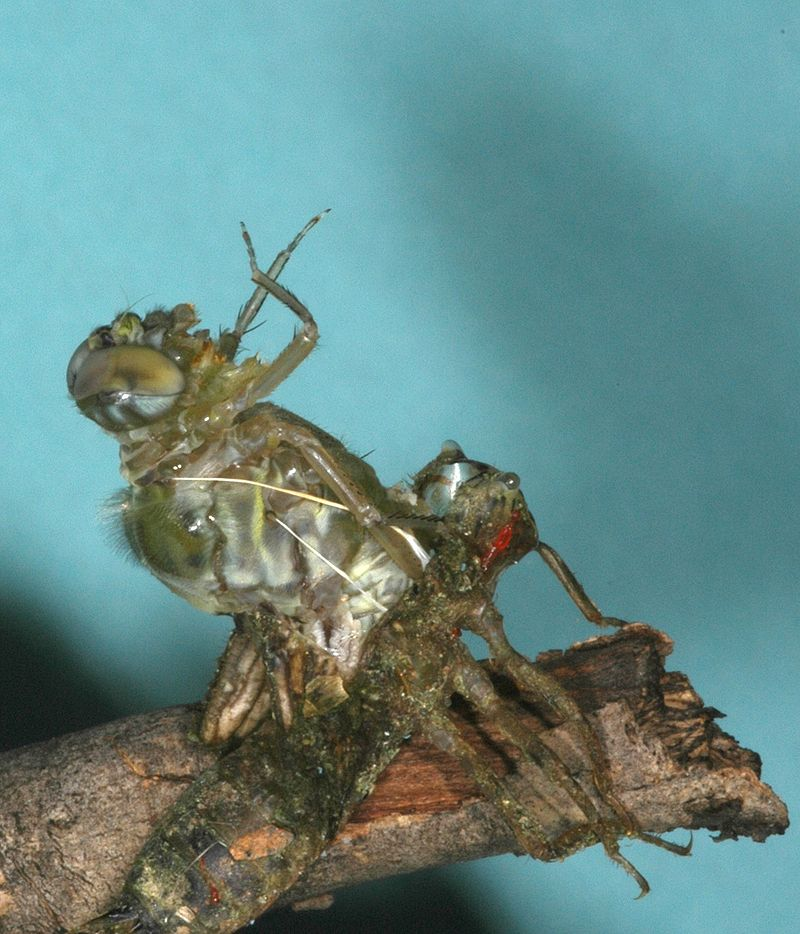

Moulting was known as mewing in medieval times
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body (often, but not always, an outer layer or covering), either at specific times of the year, or at specific points in its life cycle. In medieval times it was also…
-

Farnesol and Farnesene
Farnesol is a natural 15-carbon organic compound which is an acyclic sesquiterpene alcohol. Under standard conditions, it is a colorless liquid. It is hydrophobic, and thus insoluble in water, but miscible with oils. Farnesol is produced from 5-carbon isoprene compounds in both plants and animals. Phosphate-activated derivatives of farnesol are the building blocks of possibly all acyclic sesquiterpenoids. These compounds are doubled to…
-
β-Methylamino-L-alanine, or BMAA
β-Methylamino-L-alanine, or BMAA, is a non-proteinogenic amino acid produced by cyanobacteria. BMAA is a neurotoxin and its potential role in various neurodegenerative disorders is the subject of scientific research. Structure and properties BMAA is a derivative of the amino acid alanine with a methylamino group on the side chain. This non-proteinogenic amino acid is classified as a polar base. Sources and detection BMAA is produced by cyanobacteria in marine, freshwater, and terrestrial environments. In…
-
P300 interactions (list)
EP300 has been shown to interact with:
-
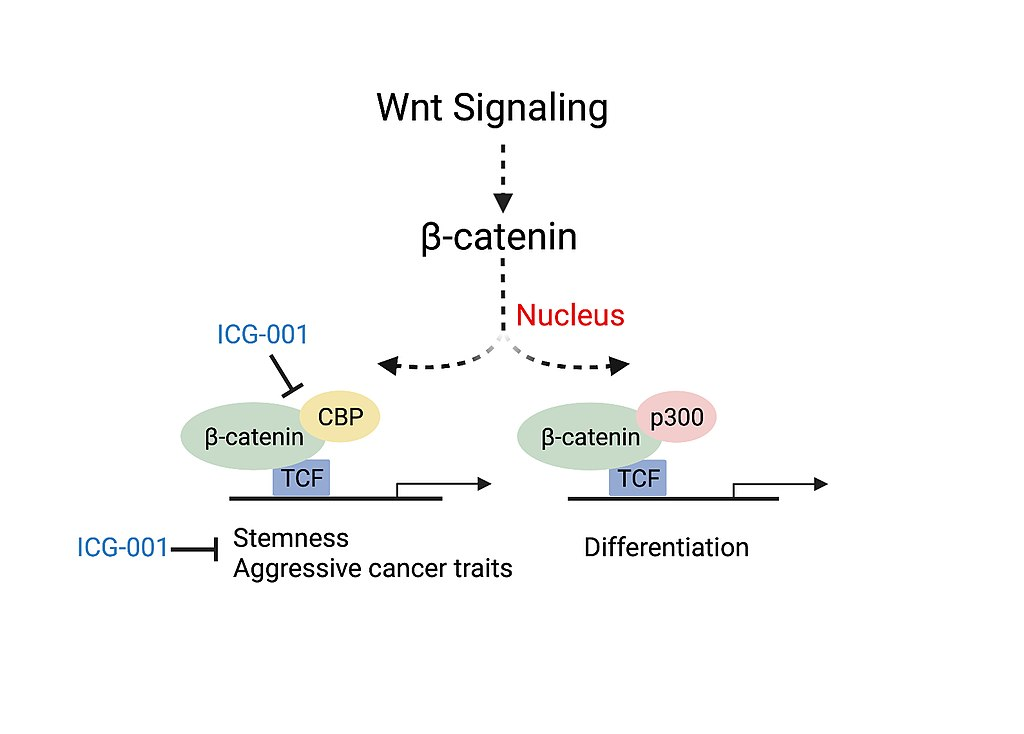
CBP has been shown to play a role in every stage of tumor development
Due to its critical role in regulation of cell proliferation, growth, migration and apoptosis, it is considered to be an oncogene, or tumor suppressor. Contrarily To date, increased CBP activity has been implicated in a variety of different malignancies including breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, colorectal cancer, acute leukemias, head and neck cancer, and many others. According to the Catalog…
-
Proteins shown to interact specifically with CBP (list)
ActrNuclear receptor coactivator ACTR is a novel histone acetyltransferase and forms a multimeric activation complex with P/CAF and CBP/p300.Karamouzis MV, Konstantinopoulos PA, Papavassiliou AG (April 2007). “Roles of CREB-binding protein (CBP)/p300 in respiratory epithelium tumorigenesis”. Cell Research. 17 (4): 324–332. doi:10.1038/cr.2007.10. PMID 17372613. S2CID 36084602.Dyson HJ, Wright PE (March 2016). “Role of Intrinsic Protein Disorder in the Function and Interactions of the Transcriptional Coactivators CREB-binding Protein (CBP)…
-
Hyperaccumulators are plants with an ability to absorb more than 100 times higher metal concentrations than typical organisms
A hyperaccumulator is a plant capable of growing in soil or water with very high concentrations of metals, absorbing these metals through their roots, and concentrating extremely high levels of metals in their tissues. The metals are concentrated at levels that are toxic to closely related species not adapted to growing on the metalliferous soils. Compared to non-hyperaccumulating species, hyperaccumulator roots…
-
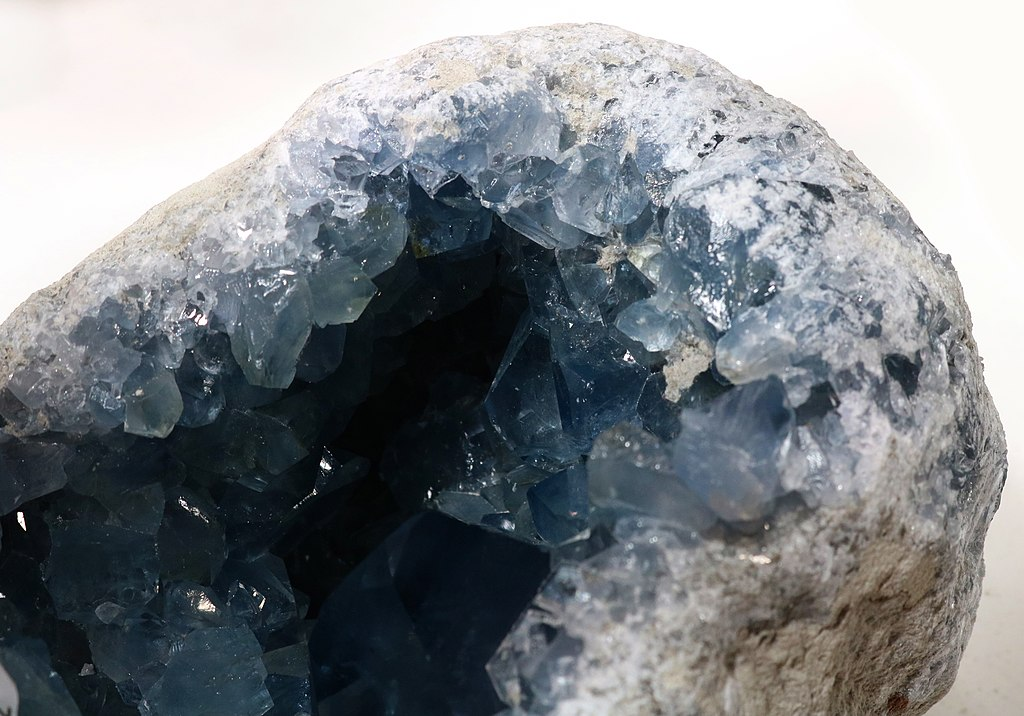

Druse, encrustation – Aggregate of crystals coating a surface or cavity, usually found in geodes
Common examples: azurite, celestine, calcite, uvarovite, malachite, quartz In geology, druse refers to a coating of fine crystals on a rock fracture surface or vein or within a vug or geode. See also References
-
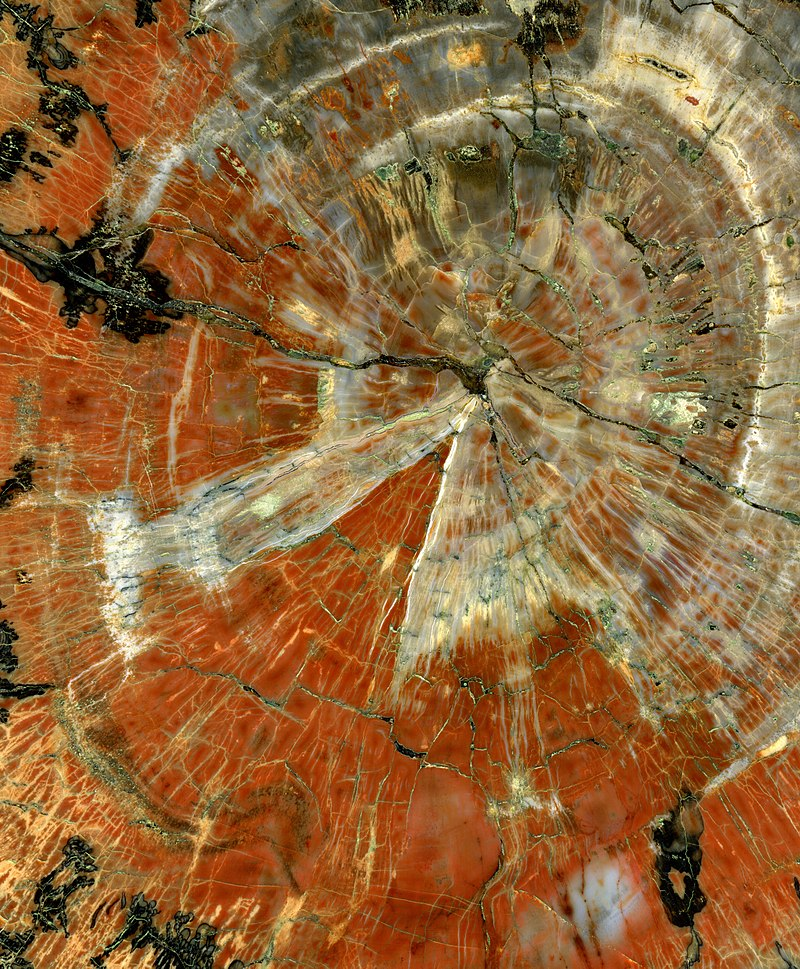
Petrified Wood
Petrified wood, also known as petrified tree (from Ancient Greek πέτρα meaning ‘rock’ or ‘stone’; literally ‘wood turned into stone’), is the name given to a special type of fossilized wood, the fossilized remains of terrestrial vegetation. Petrifaction is the result of a tree or tree-like plants having been replaced by stone via a mineralization process that often includes permineralization and replacement. The organic materials making up cell walls have been replicated…
-

Voltaic pile
Description First described in 1800 by Alessandro Volta (1745-1827), a voltaic pile consists of a series of zinc and cooper discs separated by conducting cards. The pile produces continuous electric current and was used for experiments. This voltaic pile was exhibited at the Volta Centenary Exhibition in Volta’s birthplace, Como, Italy, in 1899. A fire…
-
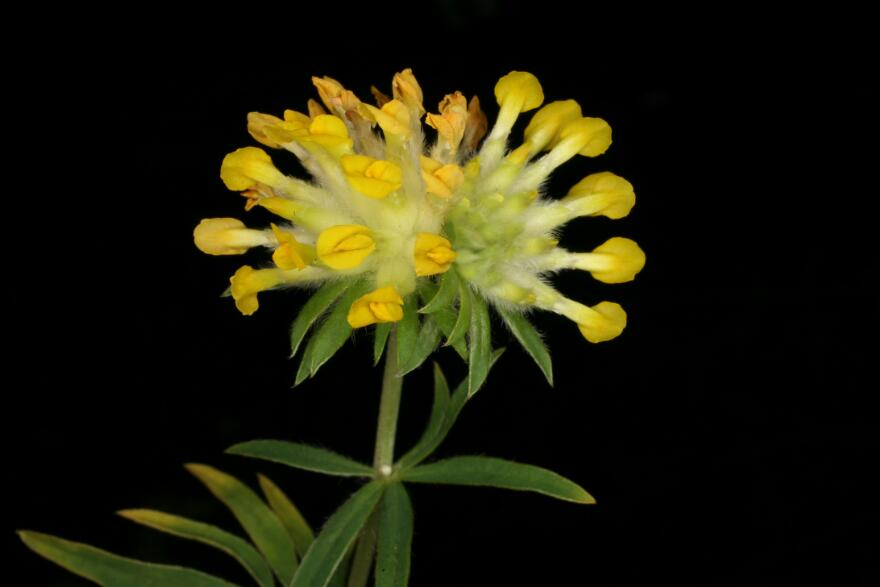

Anthyllis vulneraria L. Fabaceae. Kidney vetch, woundwort. ‘vulneraria’ means ‘wound healer’
Description (cut and paste) ‘wort’ has been used in England since the 9th century to mean root or plant. Parkinson (1640) notes Anthylis prior and Anthyllis lentisimilis (Dodoens) Anthyllis leguminosa (Lobel, Clusius) Lagopodium (Tabermontanus) Arthetica wundkraut Saxonum (Thalius) Vulneraria rustica (Gesner) and several more names from different authors. Small herb. Distribution: Europe to Iran and…
NOTES
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc

